Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Optimal Transfer With State Trigger¶
from time import perf_counter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from _sgm_test_util import LTI_plot
import condor as co
class DblInt(co.ODESystem):
A = np.array([[0, 1], [0, 0]])
B = np.array([[0], [1]])
x = state(shape=A.shape[0])
mode = state()
p1 = parameter()
p2 = parameter()
u = modal()
dynamic_output.u2 = u**2
dot[x] = A @ x + B * u
class Accel(DblInt.Mode):
condition = mode == 0.0
action[u] = 1.0
class Switch1(DblInt.Event):
function = x[0] - p1
update[mode] = 1.0
class Decel(DblInt.Mode):
condition = mode == 1.0
action[u] = -1.0
class Switch2(DblInt.Event):
function = x[0] - p2
# update[mode] = 2.
terminate = True
from scipy.optimize import bisect
class Transfer(DblInt.TrajectoryAnalysis):
initial[x] = [-9.0, 0.0]
xd = [1.0, 2.0]
Q = np.eye(2)
cost = trajectory_output(((x - xd).T @ (x - xd)) / 2)
tf = 20.0
class Options:
rootfinder = bisect
rootfinder_xtol = 1e-15
p0 = -4.0, -1.0
sim = Transfer(*p0)
# sim.implementation.callback.jac_callback(sim.implementation.callback.p, [])
class MinimumTime(co.OptimizationProblem):
p1 = variable()
p2 = variable()
sim = Transfer(p1, p2)
objective = sim.cost
class Options:
# exact_hessian = False
__implementation__ = co.implementations.ScipyCG
MinimumTime.set_initial(p1=p0[0], p2=p0[1])
t_start = perf_counter()
opt = MinimumTime()
t_stop = perf_counter()
print("time to run:", t_stop - t_start)
print(opt.p1, opt.p2)
print(opt._stats)
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.12.12/x64/lib/python3.12/site-packages/condor/implementations/iterative.py:484: RuntimeWarning: Method CG cannot handle bounds.
min_out = minimize(
time to run: 0.2351088089999962
[-3.00000001] [1.]
message: Optimization terminated successfully.
success: True
status: 0
fun: 1.5050883330650572e-17
x: [-3.000e+00 1.000e+00]
nit: 6
jac: [-3.168e-09 1.554e-14]
nfev: 14
njev: 14
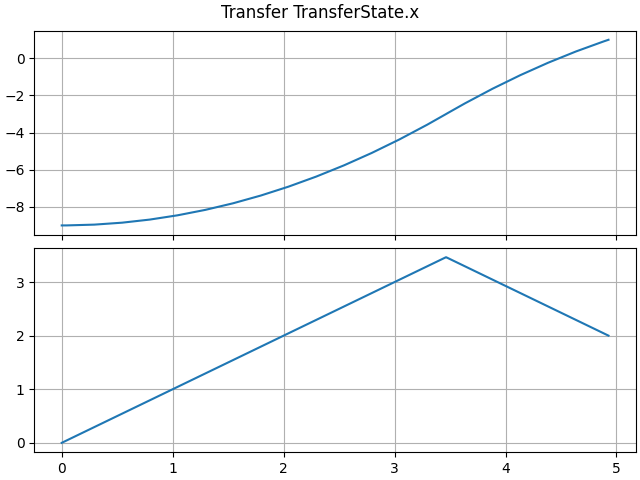
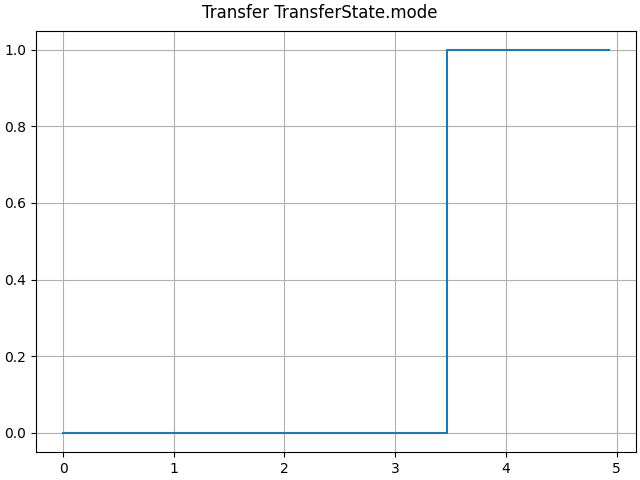
Original result:
axes = LTI_plot(opt.sim)
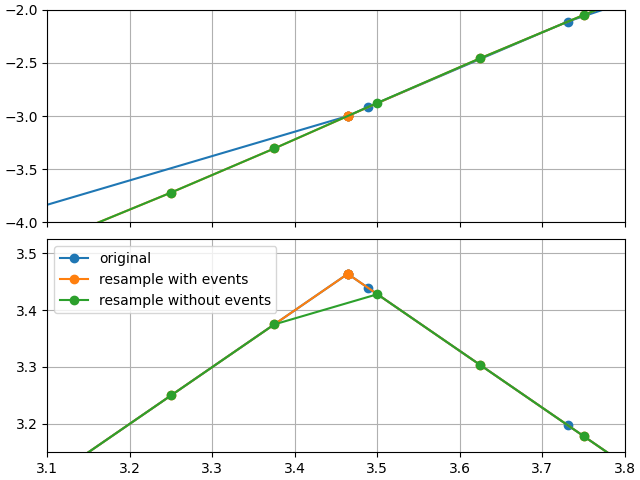
Comparing resampling results
sim_1 = opt.sim.resample(0.125)
sim_2 = opt.sim.resample(0.125, include_events=False)
sim_3 = sim_1.resample(0.125, include_events=False)
# resample always calls the original simulation result to have full fidelity
assert np.all(sim_2._res.x == sim_3._res.x)
plotting utilities
def plot_x(axes, sim, label):
for ax, x in zip(axes, sim.x):
ax.plot(sim.t, x.squeeze(), "o-", label=label)
def make_figure():
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, constrained_layout=True, sharex=True)
for ax in axes:
ax.grid(True)
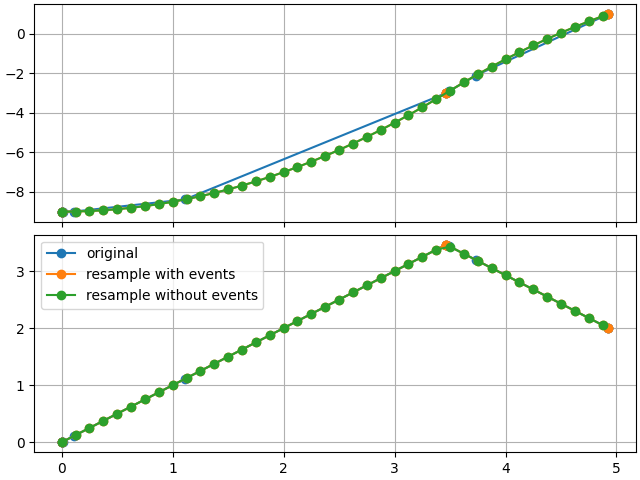
plot_x(axes, opt.sim, "original")
plot_x(axes, sim_1, "resample with events")
plot_x(axes, sim_2, "resample without events")
plt.legend()
return axes
In this case, we actually up-sampled
axes = make_figure()
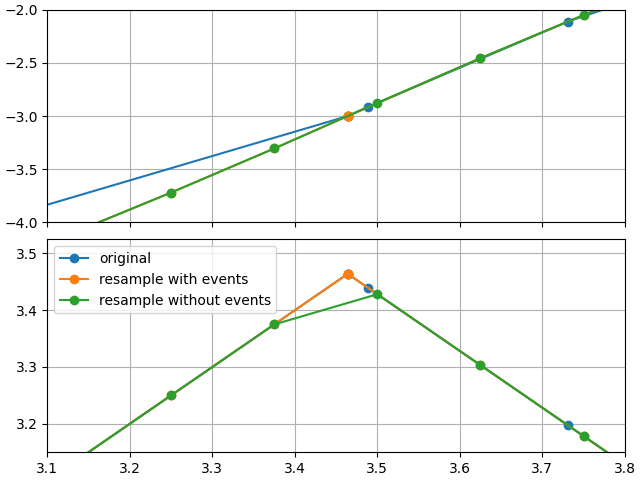
looking near the first event trigger, we see the impact of re-sampling without events
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.936 seconds)