Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Continuous Time LQR¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from _sgm_test_util import LTI_plot
import condor as co
class DblInt(co.ODESystem):
A = np.array([[0.0, 1.0], [0.0, 0.0]])
B = np.array([[0.0], [1.0]])
K = parameter(shape=(1, B.shape[0]))
x = state(shape=A.shape[0])
dynamic_output.u = -K @ x
dot[x] = A @ x + B @ u
class DblIntLQR(DblInt.TrajectoryAnalysis):
tf = 32.0
initial[x] = [1.0, 0.1]
Q = np.eye(2)
R = np.eye(1)
cost = trajectory_output(integrand=(x.T @ Q @ x + u.T @ R @ u) / 2)
class Options:
rtol = 1e-8
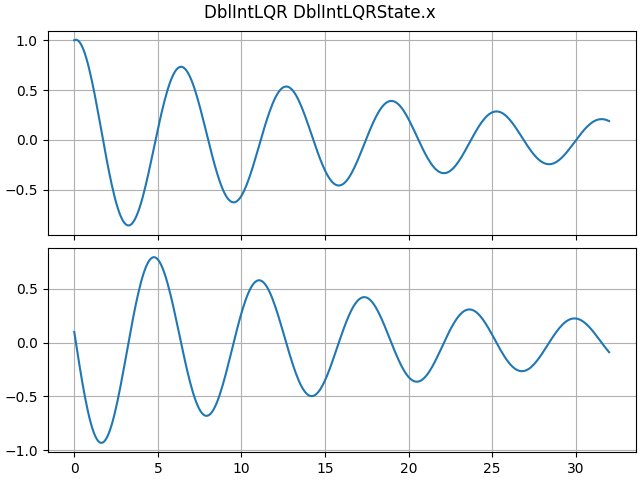
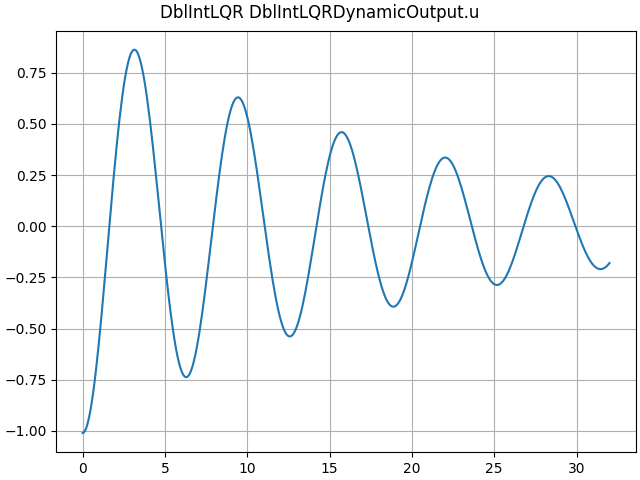
ct_sim = DblIntLQR(K=[1.0, 0.1])
LTI_plot(ct_sim)
Determine the optimal gain by embedding the trajectory analysis in an optimization problem:
class CtOptLQR(co.OptimizationProblem):
K = variable(shape=DblIntLQR.K.shape)
sim = DblIntLQR(K=K)
objective = sim.cost
class Options:
__implementation__ = co.implementations.ScipyCG
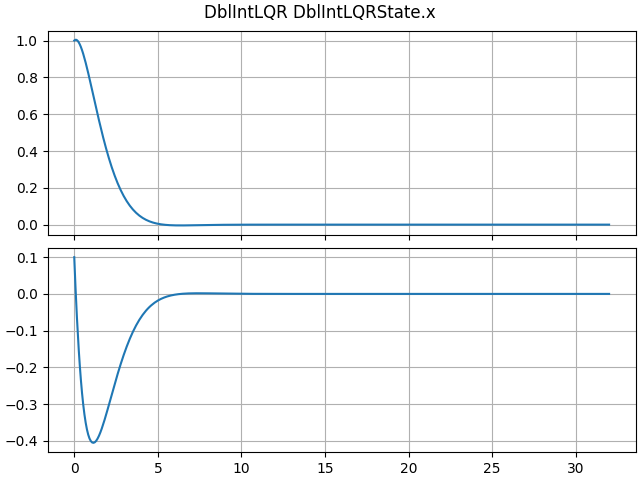
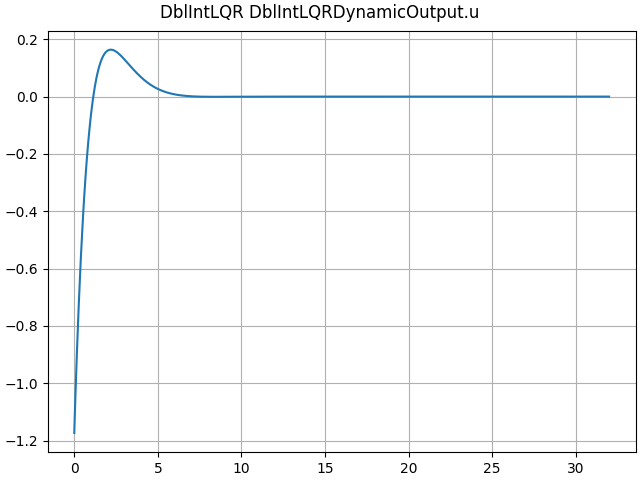
lqr_sol = CtOptLQR()
print(lqr_sol.K)
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.12.12/x64/lib/python3.12/site-packages/condor/implementations/iterative.py:484: RuntimeWarning: Method CG cannot handle bounds.
min_out = minimize(
[[1.00000506 1.73205902]]
Compare with the solution from the continuous algebraic Riccati equation:
from scipy import linalg
S = linalg.solve_continuous_are(DblIntLQR.A, DblIntLQR.B, DblIntLQR.Q, DblIntLQR.R)
K = linalg.solve(DblIntLQR.R, DblIntLQR.B.T @ S)
print(K)
[[1. 1.73205081]]
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.233 seconds)