Error Handling in Workflows
Cumulus Workflow error handling is configurable via AWS Step Function definitions, which enable users to configure what the state machine does next when an exception is thrown. Read more in the AWS docs: How Step Functions Works: Error Handling.
Cumulus Workflow Tasks should throw errors and rely on the state machine logic
to handle the error state. Errors and exceptions thrown in Cumulus Workflow
Tasks using the Cumulus Message Adapter (CMA) are caught and rethrown by the CMA
libraries unless the error name contains WorkflowError.
The former (tasks which throw errors which are not WorkflowErrors) is the
expected behavior. However a WorkflowError can be used to handle errors that
should not result in task failure.
Workflow Configuration
Some best practices for error handling in Cumulus Workflows are:
- States should include a
Catchconfiguration object which defines theResultPathto be$.exception. This passes along the entire Cumulus message to the next state with the addition of theErrorandCausedetails of the thrown error in theexceptionkey. Excluding thisCatchconfiguration means that any execution records saved for your failed workflows will not include details about the exceptions. - States may be configured to
Retrya task on specified failures to handle transient issues, such as those arising from resource allocation throttling, instead of failing the entire workflow. Cumulus supports the AWS retry configuration outlined here and an example is provided in theHelloWorldstep of theRetryPassWorkflowworkflow defined in the Cumulus repository's example workflowretry_pass_workflow. - Tasks downstream of failed tasks should understand how to pass along
exceptions if required. If a task throws an error which is caught by the
workflow configuration and passed to another state which also uses the CMA,
the CMA overrides the exception key to
"None"so the exception will not be passed to downstream tasks after the next state. This works if the exception is not needed in downstream tasks. If the exception is needed in downstream tasks, you need to re-attach the exception to the Cumulus message by setting theResultPathto be$.exceptionfor the task where the error is initially caught. In the example below,CnmResponseFailcatches and re-attaches the error to the message. - If multiple downstream tasks should run after a workflow task has thrown an error, you can create a separate failure branch of your workflow by chaining tasks that catch and re-attach the error as described above.
- Tasks that are lambdas should be configured to retry in the event of a Lambda Service Exception. See this documentation on configuring your workflow to handle transient lambda errors.
- Fail workflow state can have
CausePathandErrorPathto ensure the error properly propagated.
Example state machine definition:
{
"Comment": "Tests Workflow from Kinesis Stream",
"StartAt": "TranslateMessage",
"States": {
"TranslateMessage": {
"Parameters": {
"cma": {
"event.$": "$",
"task_config": {
"cumulus_message": {
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{$.cnm}",
"destination": "{$.meta.cnm}"
},
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.payload}"
}
]
}
}
}
},
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${aws_lambda_function.cnm_to_cma_task.arn}",
"Retry": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"Lambda.ServiceException",
"Lambda.AWSLambdaException",
"Lambda.SdkClientException"
],
"IntervalSeconds": 2,
"MaxAttempts": 6,
"BackoffRate": 2
}
],
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": ["States.ALL"],
"ResultPath": "$.exception",
"Next": "CnmResponseFail"
}
],
"Next": "SyncGranule"
},
"SyncGranule": {
"Parameters": {
"cma": {
"event.$": "$",
"ReplaceConfig": {
"Path": "$.payload",
"TargetPath": "$.payload"
},
"task_config": {
"provider": "{$.meta.provider}",
"buckets": "{$.meta.buckets}",
"collection": "{$.meta.collection}",
"downloadBucket": "{$.meta.buckets.private.name}",
"stack": "{$.meta.stack}",
"cumulus_message": {
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{$.granules}",
"destination": "{$.meta.input_granules}"
},
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.payload}"
}
]
}
}
}
},
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${module.cumulus.sync_granule_task.task_arn}",
"Retry": [
{
"ErrorEquals": ["States.ALL"],
"IntervalSeconds": 10,
"MaxAttempts": 3
}
],
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": ["States.ALL"],
"ResultPath": "$.exception",
"Next": "CnmResponseFail"
}
],
"Next": "CnmResponse"
},
"CnmResponse": {
"Parameters": {
"cma": {
"event.$": "$",
"task_config": {
"OriginalCNM": "{$.meta.cnm}",
"CNMResponseStream": "{$.meta.cnmResponseStream}",
"region": "us-east-1",
"WorkflowException": "{$.exception}",
"cumulus_message": {
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.meta.cnmResponse}"
},
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.payload}"
}
]
}
}
}
},
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${aws_lambda_function.cnm_response_task.arn}",
"Retry": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"Lambda.ServiceException",
"Lambda.AWSLambdaException",
"Lambda.SdkClientException"
],
"IntervalSeconds": 2,
"MaxAttempts": 6,
"BackoffRate": 2
}
],
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": ["States.ALL"],
"ResultPath": "$.exception",
"Next": "WorkflowFailed"
}
],
"Next": "WorkflowSucceeded"
},
"CnmResponseFail": {
"Parameters": {
"cma": {
"event.$": "$",
"task_config": {
"OriginalCNM": "{$.meta.cnm}",
"CNMResponseStream": "{$.meta.cnmResponseStream}",
"region": "us-east-1",
"WorkflowException": "{$.exception}",
"cumulus_message": {
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.meta.cnmResponse}"
},
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.payload}"
}
]
}
}
}
},
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${aws_lambda_function.cnm_response_task.arn}",
"Retry": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"Lambda.ServiceException",
"Lambda.AWSLambdaException",
"Lambda.SdkClientException"
],
"IntervalSeconds": 2,
"MaxAttempts": 6,
"BackoffRate": 2
}
],
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": ["States.ALL"],
"ResultPath": "$.exception",
"Next": "WorkflowFailed"
}
],
"Next": "WorkflowFailed"
},
"WorkflowSucceeded": {
"Type": "Succeed"
},
"WorkflowFailed": {
"Type": "Fail",
"CausePath": "$.exception.Cause",
"ErrorPath": "$.exception.Error"
}
}
}
The above results in a workflow which is visualized in the diagram below:
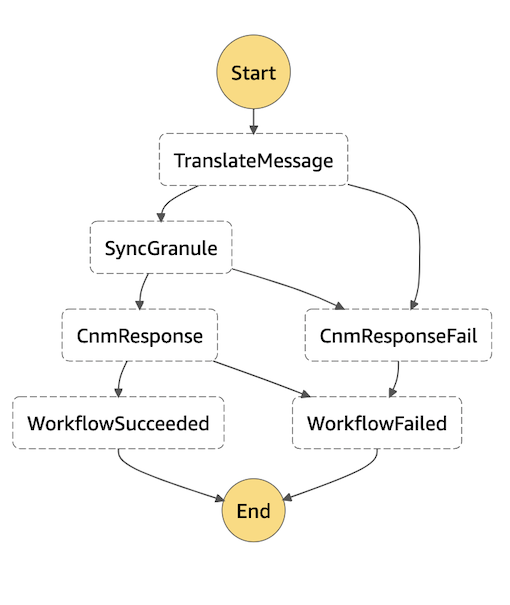
Summary
Error handling should (mostly) be the domain of workflow configuration.