Data Functionalization¶
This notebook shows how to use the Functionalize_Dataset function to easily functionalize a given dataset, even if a custom interpolator is desired. See the first cell for details on the function execution.
How to functionalize data¶
The example below shows the creation of the inputs, including example datasets with 7 dimensions. Any number of dimensions can be functionalized.
In [1]:
Copied!
from kamodo_ccmc.tools.functionalize import Functionalize_Dataset
help(Functionalize_Dataset)
from kamodo_ccmc.tools.functionalize import Functionalize_Dataset
help(Functionalize_Dataset)
Help on function Functionalize_Dataset in module kamodo_ccmc.tools.functionalize:
Functionalize_Dataset(coord_dict, data_dict, kamodo_object=None, coord_str='', func=None, func_default='data')
Determine and call the correct functionalize routine.
Inputs:
coord_dict: a dictionary containing the coordinate information.
{'name_of_coord1': {'units': 'coord1_units', 'data': coord1_data},
'name_of_coord2': {'units': 'coord2_units', 'data': coord2_data},
etc...}
coordX_data should be a 1D array. All others should be strings.
data_dict: a dictionary containing the data information.
{'variable_name1': {'units': 'data1_units', 'data': data1_array},
'variable_name2': {'units': 'data2_units', 'data': data2_array},
etc...}
dataX_array should have the same shape as
(coord1, coord2, coord3, ..., coordN)
Note:The datasets given in the data_dict dictionary should all have the
same dimensions. Datasets with different dimensions can be
functionalized by simply calling the function again with the other
dataset and the associated coordinate arrays. The datasets must
also EACH depend upon ALL of the coordinate arrays given.
coord_str: a string indicating the coordinate system of the data
(e.g. "SMcar" or "GEOsph").
kamodo_object: the previously created kamodo object. If one is not
given, then one will be created.
func: the function to be used for interpolation through the given
datasets. The function must accept values for interpolation in an
identical call structure as SciPy's RegularGridInterpolator or
interp1D. See SciPy's documentation for more information.
func_default: a string indicating whether a custom interpolation
method is dersired. The default is 'data', indicating that the
standard interpolation method will be used. Set this to 'custom' to
indicate that func is a custom interpolator.
Output: A kamodo object with the functionalized dataset.
This is similar to RU.Functionalize_Dataset, except only the gridded
interpolator is registered.
In [2]:
Copied!
# Example of functionalizing a 7D array
import numpy as np
rng1 = np.random.RandomState(1) # Seed the random generators differently
rng2 = np.random.RandomState(2) # or the arrays created below will be identical.
coord_dict = {'time': {'units': 'hr', 'data': np.linspace(0., 24., 25)},
'lon': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-180., 180., 12)},
'lat': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-90., 90., 5)},
'radius': {'units': 'R_E', 'data': np.linspace(0., 50., 10)},
'nonsense': {'units': 'm/m', 'data': np.linspace(1., 15., 15)},
'nope': {'units': 'm', 'data': np.linspace(1., 150., 25)},
'nada': {'units': 'hPa', 'data': np.linspace(0.00005, 15000., 20)}}
var_dict = {'Test_7D': {'units': 'S', 'data': rng1.rand(25, 12, 5, 10, 15, 25, 20)},
'Good_7D': {'units': 'mK', 'data': rng2.rand(25, 12, 5, 10, 15, 25, 20)}}
kamodo_object = Functionalize_Dataset(coord_dict, var_dict)
kamodo_object
# Example of functionalizing a 7D array
import numpy as np
rng1 = np.random.RandomState(1) # Seed the random generators differently
rng2 = np.random.RandomState(2) # or the arrays created below will be identical.
coord_dict = {'time': {'units': 'hr', 'data': np.linspace(0., 24., 25)},
'lon': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-180., 180., 12)},
'lat': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-90., 90., 5)},
'radius': {'units': 'R_E', 'data': np.linspace(0., 50., 10)},
'nonsense': {'units': 'm/m', 'data': np.linspace(1., 15., 15)},
'nope': {'units': 'm', 'data': np.linspace(1., 150., 25)},
'nada': {'units': 'hPa', 'data': np.linspace(0.00005, 15000., 20)}}
var_dict = {'Test_7D': {'units': 'S', 'data': rng1.rand(25, 12, 5, 10, 15, 25, 20)},
'Good_7D': {'units': 'mK', 'data': rng2.rand(25, 12, 5, 10, 15, 25, 20)}}
kamodo_object = Functionalize_Dataset(coord_dict, var_dict)
kamodo_object
Out[2]:
\begin{equation}\operatorname{Test_{7D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg],radius[R_{E}],nonsense[1],nope[m],nada[hPa])[S] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat,radius,nonsense,nope,nada \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{Good_{7D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg],radius[R_{E}],nonsense[1],nope[m],nada[hPa])[mK] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat,radius,nonsense,nope,nada \right)}\end{equation}
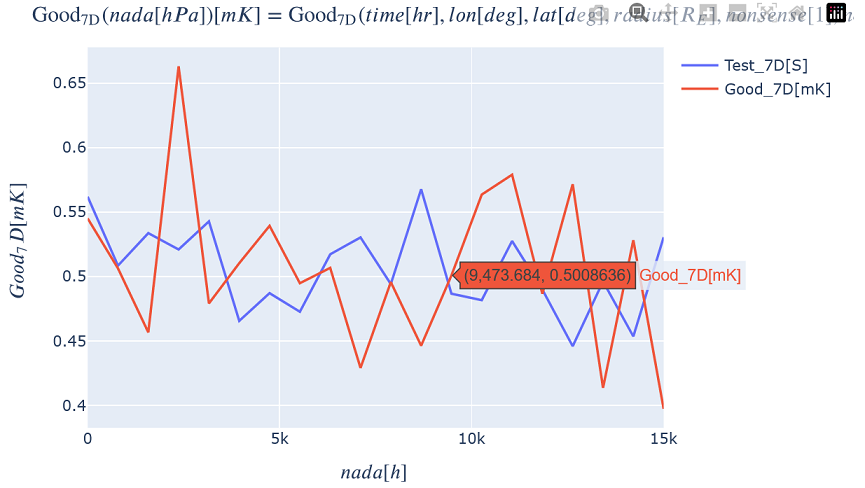
Generating a generic 1D Plot¶
Plot a 1D slice of all the variables by choosing a slice value in all but one dimension.
kamodo_object.plot('Test_7D', 'Good_7D', plot_partial={
'Test_7D': {'time': 12., 'lon': 0.5, 'lat': -20., 'radius': 15., 'nonsense': 11.5, 'nope': 5.},
'Good_7D': {'time': 12., 'lon': 0.5, 'lat': -20., 'radius': 15., 'nonsense': 11.5, 'nope': 5.}})
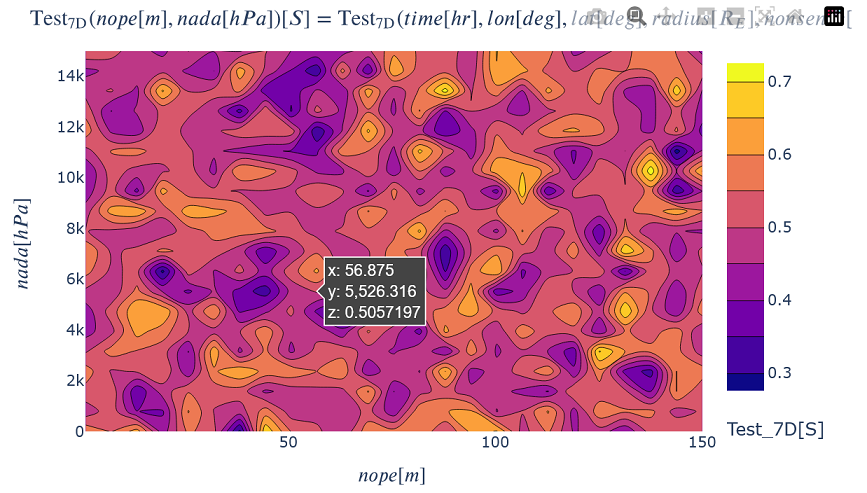
Generating a generic 2D Plot¶
Plot a 2D slice of one variable by choosing a slice value in all but two dimensions.
kamodo_object.plot('Test_7D', plot_partial={
'Test_7D': {'time': 12., 'lon': 0.5, 'lat': -20., 'radius': 15., 'nonsense': 11.5}})
Adding new functionalized datasets to a kamodo object¶
In [3]:
Copied!
# You can add datasets of other dimensions to the same kamodo_object.
coord_dict = {'time': {'units': 'hr', 'data': np.linspace(0., 24., 25)}}
var_dict = {'Test_1D': {'units': 'S', 'data': rng1.rand(25)},
'Good_1D': {'units': 'mK', 'data': rng2.rand(25)}}
kamodo_object = Functionalize_Dataset(coord_dict, var_dict, kamodo_object)
kamodo_object
# You can add datasets of other dimensions to the same kamodo_object.
coord_dict = {'time': {'units': 'hr', 'data': np.linspace(0., 24., 25)}}
var_dict = {'Test_1D': {'units': 'S', 'data': rng1.rand(25)},
'Good_1D': {'units': 'mK', 'data': rng2.rand(25)}}
kamodo_object = Functionalize_Dataset(coord_dict, var_dict, kamodo_object)
kamodo_object
Out[3]:
\begin{equation}\operatorname{Test_{7D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg],radius[R_{E}],nonsense[1],nope[m],nada[hPa])[S] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat,radius,nonsense,nope,nada \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{Good_{7D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg],radius[R_{E}],nonsense[1],nope[m],nada[hPa])[mK] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat,radius,nonsense,nope,nada \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{Test_{1D}}(time[hr])[S] = \lambda{\left(time \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{Good_{1D}}(time[hr])[mK] = \lambda{\left(time \right)}\end{equation}
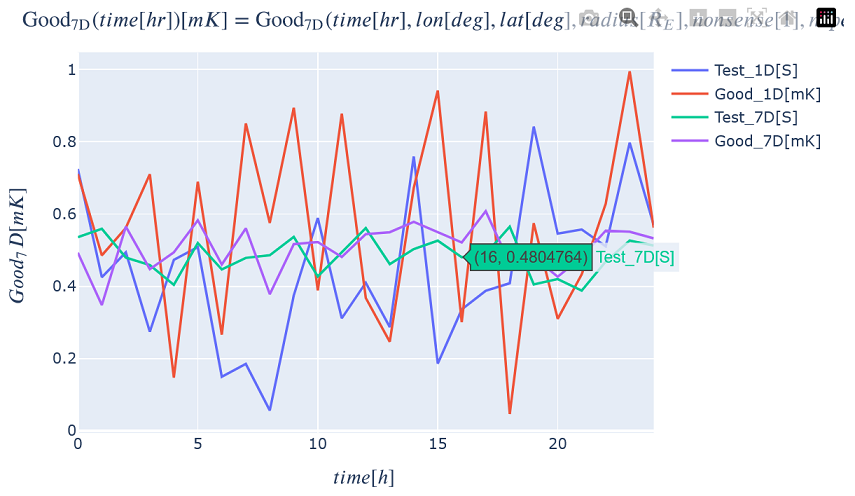
You can plot all of the functions on the same plot as long as the independent variable is the same (time in this example).
kamodo_object.plot('Test_1D', 'Good_1D', 'Test_7D', 'Good_7D', plot_partial={
'Test_7D': {'lon': 0.5, 'lat': -20., 'radius': 15., 'nonsense': 11.5, 'nope': 5., 'nada': 12.},
'Good_7D': {'lon': 0.5, 'lat': -20., 'radius': 15., 'nonsense': 11.5, 'nope': 5., 'nada': 12.}})
In [10]:
Copied!
# You even use a custom interpolator if desired for a new dataset added to the same kamodo_object.
# The interpolator must be defined separately for each dataset.
coord_dict = {'time': {'units': 'hr', 'data': np.linspace(0., 24., 25)},
'lon': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-180., 180., 12)},
'lat': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-90., 90., 5)}}
var_dict = {'TestCustomA_3D': {'units': 'S', 'data': rng1.rand(25, 12, 5)},
'TestCustomB_3D': {'units': 'm/s', 'data': rng2.rand(25, 12, 5)*-2.}}
# Define a custom interpolator (simple example)
# see https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.interpolate.RegularGridInterpolator.html
from numpy import NaN
from scipy.interpolate import RegularGridInterpolator as RGI
coord_list = [value['data'] for key, value in coord_dict.items()]
for key in var_dict.keys():
rgi = RGI(coord_list, var_dict[key]['data'], bounds_error=False,
fill_value=-10., method='nearest')
# wrap in a function and return the function
def interp(xvec):
return rgi(xvec)
tmp_dict = {key: var_dict[key]} # construct a separate dictionary for the current variable
kamodo_object = Functionalize_Dataset(coord_dict, tmp_dict, kamodo_object, func=interp, func_default='custom')
kamodo_object
# You even use a custom interpolator if desired for a new dataset added to the same kamodo_object.
# The interpolator must be defined separately for each dataset.
coord_dict = {'time': {'units': 'hr', 'data': np.linspace(0., 24., 25)},
'lon': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-180., 180., 12)},
'lat': {'units': 'deg', 'data': np.linspace(-90., 90., 5)}}
var_dict = {'TestCustomA_3D': {'units': 'S', 'data': rng1.rand(25, 12, 5)},
'TestCustomB_3D': {'units': 'm/s', 'data': rng2.rand(25, 12, 5)*-2.}}
# Define a custom interpolator (simple example)
# see https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.interpolate.RegularGridInterpolator.html
from numpy import NaN
from scipy.interpolate import RegularGridInterpolator as RGI
coord_list = [value['data'] for key, value in coord_dict.items()]
for key in var_dict.keys():
rgi = RGI(coord_list, var_dict[key]['data'], bounds_error=False,
fill_value=-10., method='nearest')
# wrap in a function and return the function
def interp(xvec):
return rgi(xvec)
tmp_dict = {key: var_dict[key]} # construct a separate dictionary for the current variable
kamodo_object = Functionalize_Dataset(coord_dict, tmp_dict, kamodo_object, func=interp, func_default='custom')
kamodo_object
Out[10]:
\begin{equation}\operatorname{Test_{7D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg],radius[R_{E}],nonsense[1],nope[m],nada[hPa])[S] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat,radius,nonsense,nope,nada \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{Good_{7D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg],radius[R_{E}],nonsense[1],nope[m],nada[hPa])[mK] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat,radius,nonsense,nope,nada \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{Test_{1D}}(time[hr])[S] = \lambda{\left(time \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{Good_{1D}}(time[hr])[mK] = \lambda{\left(time \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{TestCustomA_{3D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg])[S] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat \right)}\end{equation} \begin{equation}\operatorname{TestCustomB_{3D}}(time[hr],lon[deg],lat[deg])[m / s] = \lambda{\left(time,lon,lat \right)}\end{equation}
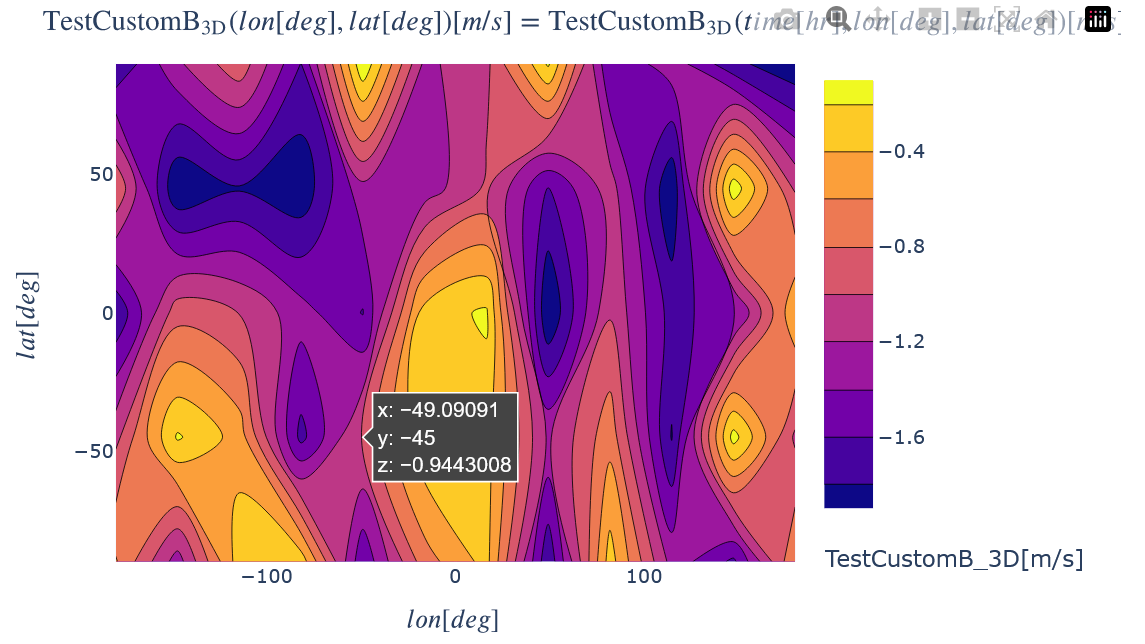
Plot a 1D slice of all the variables by choosing a slice value in all but one dimension.
kamodo_object.plot('TestCustomB_3D', plot_partial={'TestCustomB_3D':{'time': 12.56}})
Metadata functions¶
In [6]:
Copied!
# Access the metadata
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta
# Access the metadata
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta
Out[6]:
{'units': 'S',
'arg_units': {'time': 'hr'},
'citation': None,
'equation': None,
'hidden_args': []}
In [7]:
Copied!
# Add to the metadata
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta['description'] = 'Testing the functionalize.py script'
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta['citation'] = 'Ringuette et al. 2022'
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta
# Add to the metadata
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta['description'] = 'Testing the functionalize.py script'
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta['citation'] = 'Ringuette et al. 2022'
kamodo_object['Test_1D'].meta
Out[7]:
{'units': 'S',
'arg_units': {'time': 'hr'},
'citation': 'Ringuette et al. 2022',
'equation': None,
'hidden_args': [],
'description': 'Testing the functionalize.py script'}
In [8]:
Copied!
# See a pandas format output
kamodo_object.detail()
# See a pandas format output
kamodo_object.detail()
Out[8]:
| symbol | units | lhs | rhs | arg_units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test_7D | Test_7D(time, lon, lat, radius, nonsense, nope... | S | Test_7D | lambda(time, lon, lat, radius, nonsense, nope,... | {'time': 'hr', 'lon': 'deg', 'lat': 'deg', 'ra... |
| Good_7D | Good_7D(time, lon, lat, radius, nonsense, nope... | mK | Good_7D | lambda(time, lon, lat, radius, nonsense, nope,... | {'time': 'hr', 'lon': 'deg', 'lat': 'deg', 'ra... |
| Test_1D | Test_1D(time) | S | Test_1D | lambda(time) | {'time': 'hr'} |
| Good_1D | Good_1D(time) | mK | Good_1D | lambda(time) | {'time': 'hr'} |
| TestCustomA_3D | TestCustomA_3D(time, lon, lat) | S | TestCustomA_3D | lambda(time, lon, lat) | {'time': 'hr', 'lon': 'deg', 'lat': 'deg'} |
| TestCustomB_3D | TestCustomB_3D(time, lon, lat) | m/s | TestCustomB_3D | lambda(time, lon, lat) | {'time': 'hr', 'lon': 'deg', 'lat': 'deg'} |
In [9]:
Copied!
# Determine the dependent coordinates and the coordinate ranges
import kamodo_ccmc.flythrough.model_wrapper as MW
MW.Coord_Range(kamodo_object, ['Test_7D'])
# Determine the dependent coordinates and the coordinate ranges
import kamodo_ccmc.flythrough.model_wrapper as MW
MW.Coord_Range(kamodo_object, ['Test_7D'])
The minimum and maximum values for each variable and coordinate are: Test_7D: time: [0.0, 24.0, 'hr'] lon: [-180.0, 180.0, 'deg'] lat: [-90.0, 90.0, 'deg'] radius: [0.0, 50.0, 'R_E'] nonsense: [1.0, 15.0, 'm/m'] nope: [1.0, 150.0, 'm'] nada: [5e-05, 15000.0, 'hPa']