Cumulus Tasks: Message Flow
Cumulus Tasks comprise Cumulus Workflows and are either AWS Lambda tasks or AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS) activities. Cumulus Tasks permit a payload as input to the main task application code. The task payload is additionally wrapped by the Cumulus Message Adapter. The Cumulus Message Adapter supplies additional information supporting message templating and metadata management of these workflows.
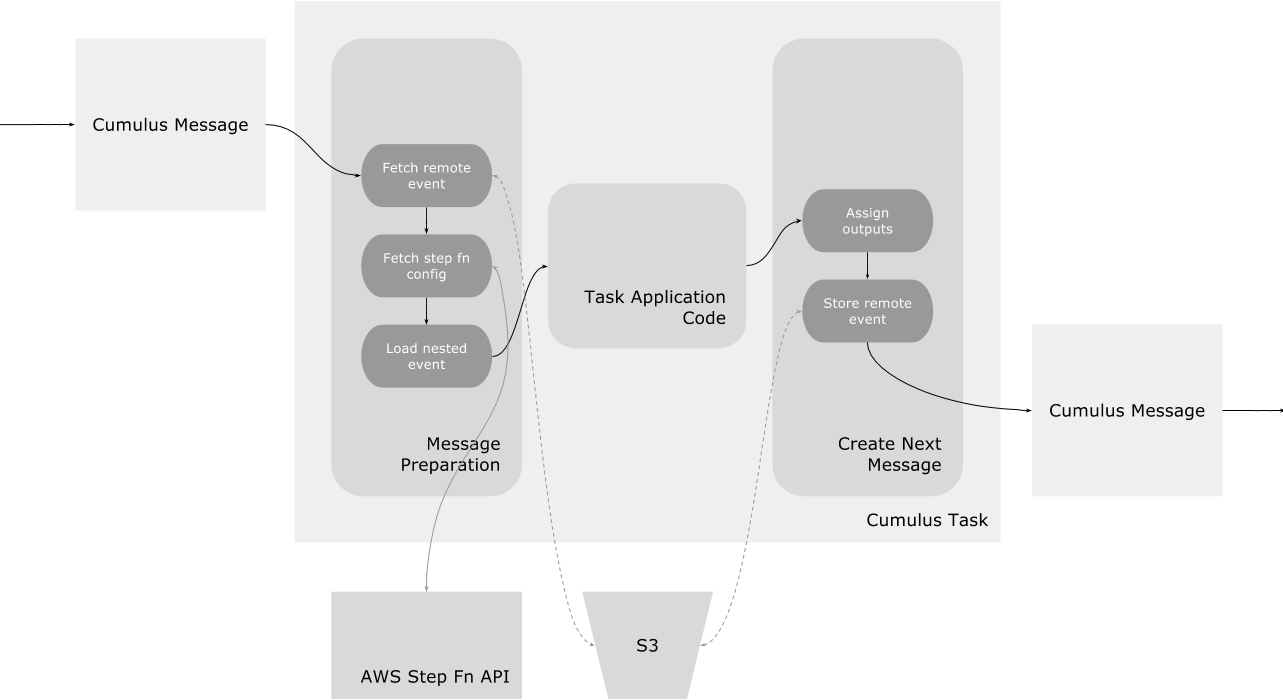
The steps in this flow are detailed in sections below.
Cumulus Message Format
Cumulus Messages come in 2 flavors: The full Cumulus Message and the Cumulus Remote Message. The Cumulus Remote Message points to a full Cumulus Message stored in S3 because of size limitations.
A full Cumulus Message has the 4 following keys:
workflow_config: Definition-time information to set up tasks. Optionally includes configuration for each task in the workflow, keyed by task name.cumulus_meta: System runtime information that should generally not be touched outside of Cumulus library code or the Cumulus Message Adapter. Stores meta information about the workflow such as the state machine name and the current workflow execution's name. This information is used to look up the current active task. The name of the current active task is used to look up the corresponding task's config inworkflow_config.meta: Runtime information captured by the workflow operators. Stores execution-agnostic variables which can be re-used via templates inworkflow_config.payload: Payload is runtime information for the tasks.
Here's a simple example of a Cumulus Message:
{
"workflow_config": {
"Example": {
"inlinestr": "prefix{meta.foo}suffix",
"array": "{[$.meta.foo]}",
"object": "{{$.meta}}"
}
},
"cumulus_meta": {
"message_source": "sfn",
"state_machine": "arn:aws:states:us-east-1:1234:stateMachine:MySfn",
"execution_name": "MyExecution__id-1234",
"id": "id-1234"
},
"meta": {
"foo": "bar"
},
"payload": {
"anykey": "anyvalue"
}
}
A Cumulus Remote Message has only the keys replace and cumulus_meta.
{
"replace": {
"Bucket": "cumulus-bucket",
"Key": "my-large-event.json"
},
"cumulus_meta": {}
}
Cumulus Message Preparation
The event coming into a Cumulus Task is assumed to be a Cumulus Message or Cumulus Remote Message and should first be handled by the functions described below before being passed to the task application code.
Preparation Step 1: Fetch remote event
Fetch remote event will fetch the full event from S3 if the cumulus message includes a replace key.
Once "my-large-event.json" is fetched from S3, it's returned from the fetch remote event function. If no "replace" key is present, the event passed to the fetch remote event function is assumed to be a full Cumulus Message and returned as-is.
Preparation Step 2: Fetch step function config
Fetch step function config determines what current task is being executed. Note this is different from what lambda or activity is being executed, because the same lambda or activity can be used for different tasks. The current task name is used to load the appropriate configuration from the Cumulus Message's 'workflow_config'.
Preparation Step 3: Load nested event
Using the config returned from the previous step, load nested event resolves templates for the final config and input to send to the task's application code. Read more on URL Templating in the Protocol section.
Task Application Code
After message prep, the message passed to the task application code is of the form:
{
"input": {},
"config": {}
}
Create Next Message functions
Whatever comes out of the task application code is used to construct an outgoing Cumulus Message.
Create Next Message Step 1: Assign outputs
The config loaded from the Fetch step function config step may have a cumulus_message key. This can be used to "dispatch" fields from the task's application output to a destination in the final event output (via URL templating). Here's an example where the value of input.anykey would be dispatched as the value of payload.out in the final cumulus message:
{
"workflow_config": {
"Example": {
"bar": "baz",
"cumulus_message": {
"input": "{{$.payload.input}}",
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{{$.input.anykey}}",
"destination": "{{$.payload.out}}"
}
]
}
}
},
"cumulus_meta": {
"task": "Example",
"message_source": "local",
"id": "id-1234"
},
"meta": {
"foo": "bar"
},
"payload": {
"input": {
"anykey": "anyvalue"
}
}
}
Create Next Message Step 2: Store remote event
Store remote event complements Fetch remote event: If the cumulus message is too big, it will be stored in S3 and the final output of the task will be Cumulus Remove Message - an object with only the replace and cumulus_meta keys. The replace key identifies where the large event has been stored in S3.