CNM Workflow
This entry documents how to setup a workflow that utilizes the built-in CNM/Kinesis functionality in Cumulus.
Prior to working through this entry you should be familiar with the Cloud Notification Mechanism.
Sections
Prerequisites
Cumulus
This entry assumes you have a deployed instance of Cumulus (version >= 1.16.0). The entry assumes you are deploying Cumulus via the cumulus terraform module sourced from the release page.
AWS CLI
This entry assumes you have the AWS CLI installed and configured. If you do not, please take a moment to review the documentation - particularly the examples relevant to Kinesis - and install it now.
Kinesis
This entry assumes you already have two Kinesis data steams created for use as CNM notification and response data streams.
If you do not have two streams setup, please take a moment to review the Kinesis documentation and setup two basic single-shard streams for this example:
Using the "Create Data Stream" button on the Kinesis Dashboard, work through the dialogue.
You should be able to quickly use the "Create Data Stream" button on the Kinesis Dashboard, and setup streams that are similar to the following example:
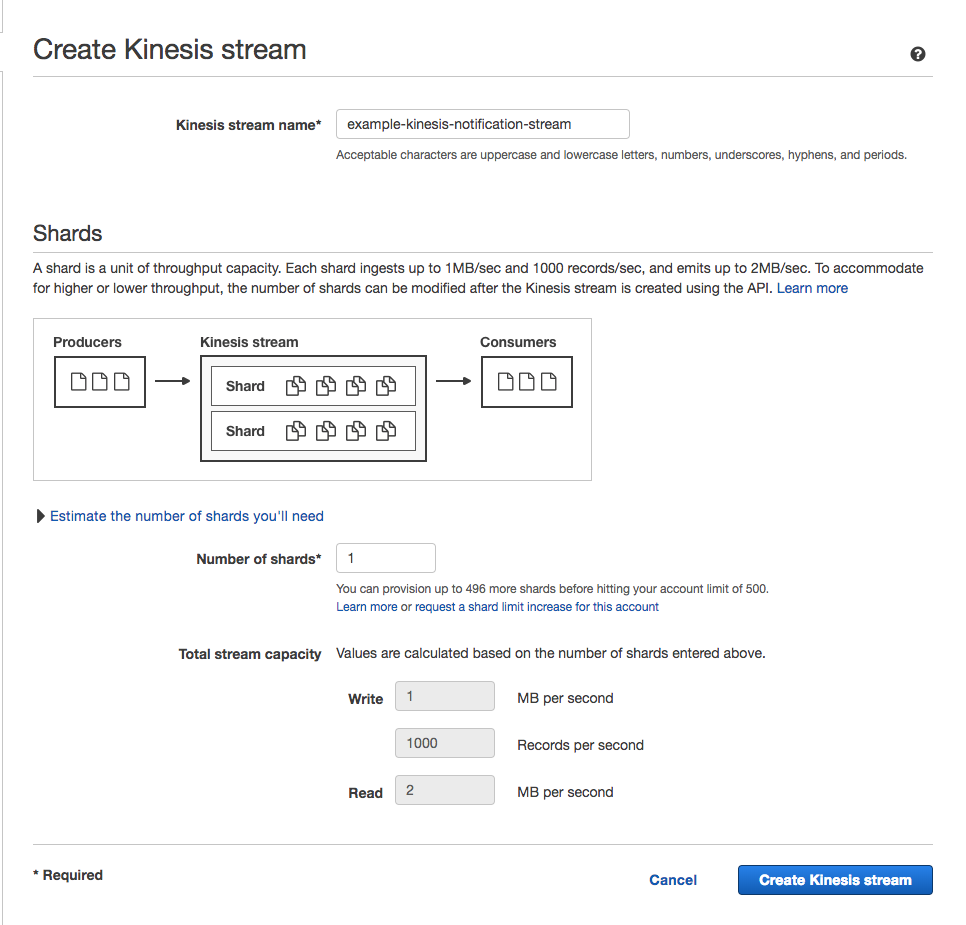
Please bear in mind that your {{prefix}}-lambda-processing IAM role will need permissions to write to the response stream for this workflow to succeed if you create the Kinesis stream with a dashboard user. If you are using the cumulus top-level module for your deployment this should be set properly.
If not, the most straightforward approach is to attach the AmazonKinesisFullAccess policy for the stream resource to whatever role your Lambda
s are using, however your environment/security policies may require an approach specific to your deployment environment.
In operational environments it's likely science data providers would typically be responsible for providing a Kinesis stream with the appropriate permissions.
For more information on how this process works and how to develop a process that will add records to a stream, read the Kinesis documentation and the developer guide.
Source Data
This entry will run the SyncGranule task against a single target data file. To that end it will require a single data file to be present in an S3 bucket matching the Provider configured in the next section.
Collection and Provider
Cumulus will need to be configured with a Collection and Provider entry of your choosing. The provider should match the location of the source data from the Ingest Source Data section.
This can be done via the Cumulus Dashboard if installed or the API. It is strongly recommended to use the dashboard if possible.
Configure the Workflow
Provided the prerequisites have been fulfilled, you can begin adding the needed values to your Cumulus configuration to configure the example workflow.
The following are steps that are required to set up your Cumulus instance to run the example workflow:
Example CNM Workflow
In this example, we're going to trigger a workflow by creating a Kinesis rule and sending a record to a Kinesis stream.
The following workflow definition should be added to a new .tf workflow resource (e.g. cnm_workflow.tf) in your deployment directory. For the complete CNM workflow example, see examples/cumulus-tf/cnm_workflow.tf.
Add the following to the new terraform file in your deployment directory, updating the following:
- Set the
response-endpointkey in theCnmResponsetask in the workflow JSON to match the name of the Kinesis response stream you configured in the prerequisites section - Update the
sourcekey to the workflow module to match the Cumulus release associated with your deployment.
module "cnm_workflow" {
source = "https://github.com/nasa/cumulus/releases/download/{version}/terraform-aws-cumulus-workflow.zip"
prefix = var.prefix
name = "CNMExampleWorkflow"
workflow_config = module.cumulus.workflow_config
system_bucket = var.system_bucket
{
state_machine_definition = <<JSON
"CNMExampleWorkflow": {
"Comment": "CNMExampleWorkflow",
"StartAt": "TranslateMessage",
"States": {
"TranslateMessage": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${aws_lambda_function.cnm_to_cma_task.arn}",
"Parameters": {
"cma": {
"event.$": "$",
"task_config": {
"collection": "{$.meta.collection}",
"cumulus_message": {
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{$.cnm}",
"destination": "{$.meta.cnm}"
},
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.payload}"
}
]
}
}
}
},
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"States.ALL"
],
"ResultPath": "$.exception",
"Next": "CnmResponse"
}
],
"Next": "SyncGranule"
},
"SyncGranule": {
"Parameters": {
"cma": {
"event.$": "$",
"task_config": {
"provider": "{$.meta.provider}",
"buckets": "{$.meta.buckets}",
"collection": "{$.meta.collection}",
"downloadBucket": "{$.meta.buckets.private.name}",
"stack": "{$.meta.stack}",
"cumulus_message": {
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{$.granules}",
"destination": "{$.meta.input_granules}"
},
{
"source": "{$}",
"destination": "{$.payload}"
}
]
}
}
}
},
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${module.cumulus.sync_granule_task.task_arn}",
"Retry": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"States.ALL"
],
"IntervalSeconds": 10,
"MaxAttempts": 3
}
],
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"States.ALL"
],
"ResultPath": "$.exception",
"Next": "CnmResponse"
}
],
"Next": "CnmResponse"
},
"CnmResponse": {
"Parameters": {
"cma": {
"event.$": "$",
"task_config": {
"OriginalCNM": "{$.meta.cnm}",
"distribution_endpoint": "{$.meta.distribution_endpoint}",
"response-endpoint": "ADD YOUR RESPONSE STREAM NAME HERE",
"region": "us-east-1",
"type": "kinesis",
"WorkflowException": "{$.exception}",
"cumulus_message": {
"outputs": [
{
"source": "{$.cnm}",
"destination": "{$.meta.cnmResponse}"
},
{
"source": "{$.input.input}",
"destination": "{$.payload}"
}
]
}
}
}
},
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${aws_lambda_function.cnm_response_task.arn}",
"Retry": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"States.ALL"
],
"IntervalSeconds": 5,
"MaxAttempts": 3
}
],
"End": true
}
}
}
}
JSON
Again, please make sure to modify the value response-endpoint to match the stream name (not ARN) for your Kinesis response stream.
Lambda Configuration
To execute this workflow, you're required to include several Lambda resources in your deployment. To do this, add the following task (Lambda) definitions to your deployment along with the workflow you created above:
- https://github.com/nasa/cumulus/blob/master/example/cumulus-tf/cnm_to_cma_task.tf
- https://github.com/nasa/cumulus/blob/master/example/cumulus-tf/cnm_response_task.tf
To utilize these tasks you need to ensure you have a compatible CMA layer. See the deployment instructions for more details on how to deploy a CMA layer.
CNMToCMA: https://github.com/podaac/cumulus-cnm-to-granuleCnmResponse: https://github.com/podaac/cumulus-cnm-response-task
Below is a description of each of these tasks:
CNMToCMA
CNMToCMA is meant for the beginning of a workflow: it maps CNM granule information to a payload for downstream tasks. For other CNM workflows, you would need to ensure that downstream tasks in your workflow either understand the CNM message or include a translation task like this one.
You can also manipulate the data sent to downstream tasks using task_config for various states in your workflow resource configuration. Read more about how to configure data on the Workflow Input & Output page.
CnmResponse
The CnmResponse Lambda generates a CNM response message and puts it on the response-endpoint Kinesis stream.
You can read more about the expected schema of a CnmResponse record in the Cloud Notification Mechanism schema repository.
Additional Tasks
Lastly, this entry also makes use of the SyncGranule task from the cumulus module.
Redeploy
Once the above configuration changes have been made, redeploy your stack.
Please refer to Update Cumulus resources in the deployment documentation if you are unfamiliar with redeployment.
Rule Configuration
Cumulus includes a messageConsumer Lambda function (message-consumer). Cumulus kinesis-type rules create the event source mappings between Kinesis streams and the messageConsumer Lambda. The messageConsumer Lambda consumes records from one or more Kinesis streams, as defined by enabled kinesis-type rules. When new records are pushed to one of these streams, the messageConsumer triggers workflows associated with the enabled kinesis-type rules.
To add a rule via the dashboard (if you'd like to use the API, see the docs here), navigate to the Rules page and click Add a rule, then configure the new rule using the following template (substituting correct values for parameters denoted by ${}):
{
"collection": {
"name": "L2_HR_PIXC",
"version": "000"
},
"name": "L2_HR_PIXC_kinesisRule",
"provider": "PODAAC_SWOT",
"rule": {
"type": "kinesis",
"value": "arn:aws:kinesis:{{awsRegion}}:{{awsAccountId}}:stream/{{streamName}}"
},
"state": "ENABLED",
"workflow": "CNMExampleWorkflow"
}
- The rule's
valueattribute value must match the Amazon Resource Name ARN for the Kinesis data stream you've preconfigured. You should be able to obtain this ARN from the Kinesis Dashboard entry for the selected stream. - The collection and provider should match the collection and provider you setup in the
Prerequisitessection.
Once you've clicked on 'submit' a new rule should appear in the dashboard's Rule Overview.
Execute the Workflow
Once Cumulus has been redeployed and a rule has been added, we're ready to trigger the workflow and watch it execute.
How to Trigger the Workflow
To trigger matching workflows, you will need to put a record on the Kinesis stream that the message-consumer Lambda will recognize as a matching event. Most importantly, it should include a collection name that matches a valid collection.
For the purpose of this example, the easiest way to accomplish this is using the AWS CLI.
Create Record JSON
Construct a JSON file containing an object that matches the values that have been previously setup. This JSON object should be a valid Cloud Notification Mechanism message.
This example is somewhat contrived, as the downstream tasks don't care about most of these fields. A 'real' data ingest workflow would.
The following values (denoted by ${} in the sample below) should be replaced to match values we've previously configured:
TEST_DATA_FILE_NAME: The filename of the test data that is available in the S3 (or other) provider we created earlier.TEST_DATA_URI: The full S3 path to the test data (e.g. s3://bucket-name/path/granule)COLLECTION: The collection name defined in the prerequisites for this product
{
"product": {
"files": [
{
"checksumType": "md5",
"name": "${TEST_DATA_FILE_NAME}",
"checksum": "bogus_checksum_value",
"uri": "${TEST_DATA_URI}",
"type": "data",
"size": 12345678
}
],
"name": "${TEST_DATA_FILE_NAME}",
"dataVersion": "006"
},
"identifier ": "testIdentifier123456",
"collection": "${COLLECTION}",
"provider": "TestProvider",
"version": "001",
"submissionTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:29.791198"
}
Add Record to Kinesis Data Stream
Using the JSON file you created, push it to the Kinesis notification stream:
aws kinesis put-record --stream-name YOUR_KINESIS_NOTIFICATION_STREAM_NAME_HERE --partition-key 1 --data file:///path/to/file.json
The above command uses the stream name, not the ARN.
The command should return output similar to:
{
"ShardId": "shardId-000000000000",
"SequenceNumber": "42356659532578640215890215117033555573986830588739321858"
}
This command will put a record containing the JSON from the --data flag onto the Kinesis data stream. The messageConsumer Lambda will consume the record and construct a valid CMA payload to trigger workflows. For this example, the record will trigger the CNMExampleWorkflow workflow as defined by the rule previously configured.
You can view the current running executions on the Executions dashboard page which presents a list of all executions, their status (running, failed, or completed), to which workflow the execution belongs, along with other information.
Verify Workflow Execution
As detailed above, once the record is added to the Kinesis data stream, the messageConsumer Lambda will trigger the CNMExampleWorkflow .
TranslateMessage
TranslateMessage (which corresponds to the CNMToCMA Lambda) will take the CNM object payload and add a granules object to the CMA payload that's consistent with other Cumulus ingest tasks, and add a meta.cnm key (as well as the payload) to store the original message.
For more on the Message Adapter, please see the Message Flow documentation.
An example of what is happening in the CNMToCMA Lambda is as follows:
Example Input Payload:
"payload": {
"identifier ": "testIdentifier123456",
"product": {
"files": [
{
"checksumType": "md5",
"name": "MOD09GQ.A2016358.h13v04.006.2016360104606.hdf",
"checksum": "bogus_checksum_value",
"uri": "s3://some_bucket/cumulus-test-data/pdrs/MOD09GQ.A2016358.h13v04.006.2016360104606.hdf",
"type": "data",
"size": 12345678
}
],
"name": "TestGranuleUR",
"dataVersion": "006"
},
"version": "123456",
"collection": "MOD09GQ",
"provider": "TestProvider",
"submissionTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:29.791198"
}
Example Output Payload:
"payload": {
"cnm": {
"identifier ": "testIdentifier123456",
"product": {
"files": [
{
"checksumType": "md5",
"name": "MOD09GQ.A2016358.h13v04.006.2016360104606.hdf",
"checksum": "bogus_checksum_value",
"uri": "s3://some-bucket/cumulus-test-data/data/MOD09GQ.A2016358.h13v04.006.2016360104606.hdf",
"type": "data",
"size": 12345678
}
],
"name": "TestGranuleUR",
"dataVersion": "006"
},
"version": "123456",
"collection": "MOD09GQ",
"provider": "TestProvider",
"submissionTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:29.791198",
"receivedTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:31.634552"
},
"output": {
"granules": [
{
"granuleId": "TestGranuleUR",
"files": [
{
"path": "some-bucket/data",
"url_path": "s3://some-bucket/cumulus-test-data/data/MOD09GQ.A2016358.h13v04.006.2016360104606.hdf",
"bucket": "some-bucket",
"name": "MOD09GQ.A2016358.h13v04.006.2016360104606.hdf",
"size": 12345678
}
]
}
]
}
}
SyncGranules
This Lambda will take the files listed in the payload and move them to s3://{deployment-private-bucket}/file-staging/{deployment-name}/{COLLECTION}/{file_name}.
CnmResponse
Assuming a successful execution of the workflow, this task will recover the meta.cnm key from the CMA output, and add a "SUCCESS" record to the notification Kinesis stream.
If a prior step in the workflow has failed, this will add a "FAILURE" record to the stream instead.
The data written to the response-endpoint should adhere to the Response Message Fields schema.
Example CNM Success Response:
{
"provider": "PODAAC_SWOT",
"collection": "SWOT_Prod_l2:1",
"processCompleteTime": "2017-09-30T03:45:29.791198",
"submissionTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:29.791198",
"receivedTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:31.634552",
"identifier": "1234-abcd-efg0-9876",
"response": {
"status": "SUCCESS"
}
}
Example CNM Error Response:
{
"provider": "PODAAC_SWOT",
"collection": "SWOT_Prod_l2:1",
"processCompleteTime": "2017-09-30T03:45:29.791198",
"submissionTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:29.791198",
"receivedTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:31.634552",
"identifier": "1234-abcd-efg0-9876",
"response": {
"status": "FAILURE",
"errorCode": "PROCESSING_ERROR",
"errorMessage": "File [cumulus-dev-a4d38f59-5e57-590c-a2be-58640db02d91/prod_20170926T11:30:36/production_file.nc] did not match gve checksum value."
}
}
Note the CnmResponse state defined in the .tf workflow definition above configures $.exception to be passed to the CnmResponse Lambda keyed under config.WorkflowException. This is required for the CnmResponse code to deliver a failure response.
To test the failure scenario, send a record missing the product.name key.
Verify results
Check for successful execution on the dashboard
Following the successful execution of this workflow, you should expect to see the workflow complete successfully on the dashboard:
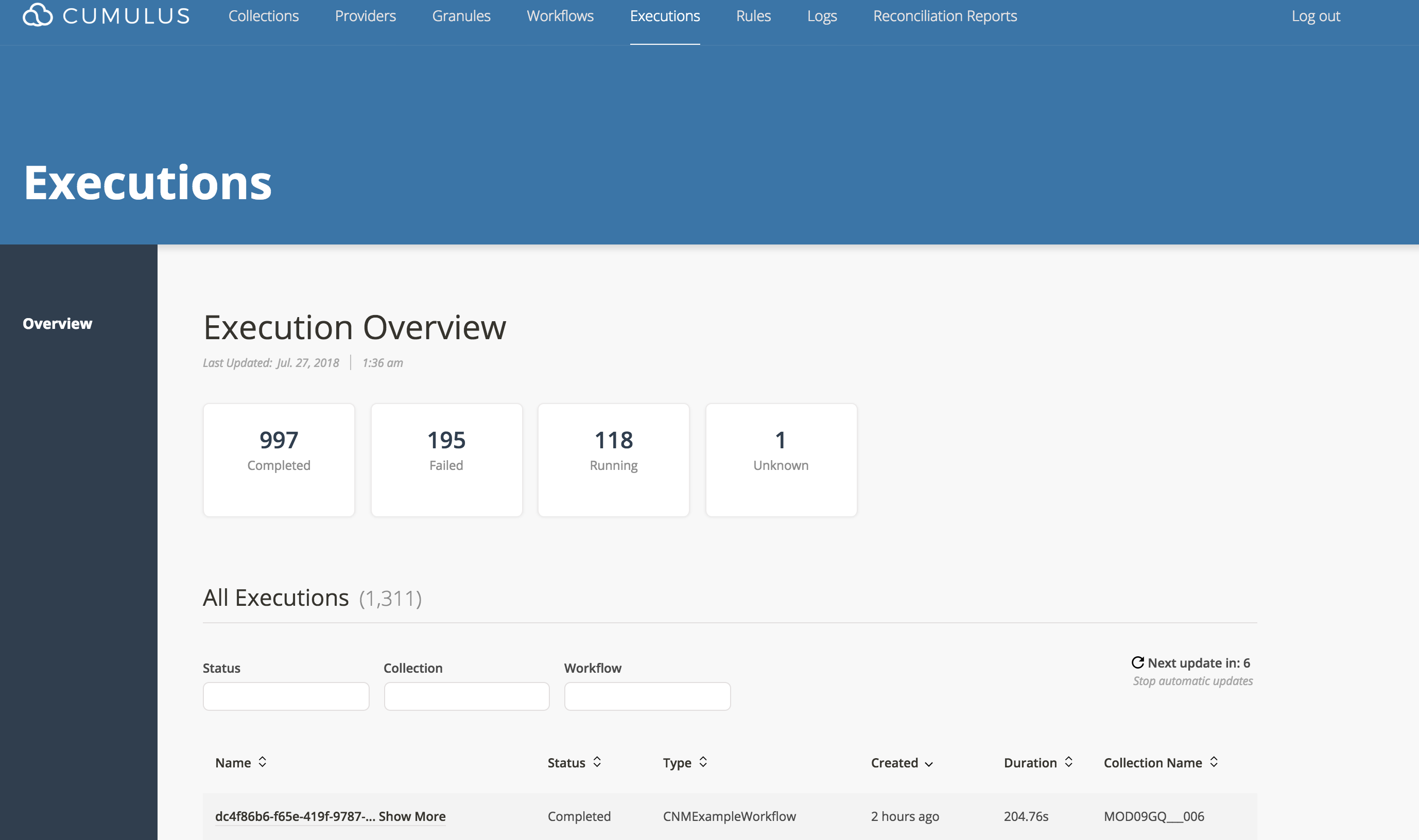
Check the test granule has been delivered to S3 staging
The test granule identified in the Kinesis record should be moved to the deployment's private staging area.
Check for Kinesis records
A SUCCESS notification should be present on the response-endpoint Kinesis stream.
You should be able to validate the notification and response streams have the expected records with the following steps (the AWS CLI Kinesis Basic Stream Operations is useful to review before proceeding):
Get a shard iterator (substituting your stream name as appropriate):
aws kinesis get-shard-iterator \
--shard-id shardId-000000000000 \
--shard-iterator-type LATEST \
--stream-name NOTIFICATION_OR_RESPONSE_STREAM_NAME
which should result in an output to:
{
"ShardIterator": "VeryLongString=="
}
- Re-trigger the workflow by using the
put-recordcommand from - As the workflow completes, use the output from the
get-shard-iteratorcommand to request data from the stream:
aws kinesis get-records --shard-iterator SHARD_ITERATOR_VALUE
This should result in output similar to:
{
"Records": [
{
"SequenceNumber": "49586720336541656798369548102057798835250389930873978882",
"ApproximateArrivalTimestamp": 1532664689.128,
"Data": "eyJpZGVudGlmaWVyICI6InRlc3RJZGVudGlmaWVyMTIzNDU2IiwidmVyc2lvbiI6IjAwNiIsImNvbGxlY3Rpb24iOiJNT0QwOUdRIiwicHJvdmlkZXIiOiJUZXN0UHJvdmlkZXIiLCJwcm9kdWN0U2l6ZSI6MTkwODYzNS4wLCJyZXNwb25zZSI6eyJzdGF0dXMiOiJTVUNDRVNTIn0sInByb2Nlc3NDb21wbGV0ZVRpbWUiOiIyMDE4LTA3LTI3VDA0OjExOjI4LjkxOSJ9",
"PartitionKey": "1"
},
{
"SequenceNumber": "49586720336541656798369548102059007761070005796999266306",
"ApproximateArrivalTimestamp": 1532664707.149,
"Data": "eyJpZGVudGlmaWVyICI6InRlc3RJZGVudGlmaWVyMTIzNDU2IiwidmVyc2lvbiI6IjAwNiIsImNvbGxlY3Rpb24iOiJNT0QwOUdRIiwicHJvdmlkZXIiOiJUZXN0UHJvdmlkZXIiLCJwcm9kdWN0U2l6ZSI6MTkwODYzNS4wLCJyZXNwb25zZSI6eyJzdGF0dXMiOiJTVUNDRVNTIn0sInByb2Nlc3NDb21wbGV0ZVRpbWUiOiIyMDE4LTA3LTI3VDA0OjExOjQ2Ljk1OCJ9",
"PartitionKey": "1"
}
],
"NextShardIterator": "AAAAAAAAAAFo9SkF8RzVYIEmIsTN+1PYuyRRdlj4Gmy3dBzsLEBxLo4OU+2Xj1AFYr8DVBodtAiXbs3KD7tGkOFsilD9R5tA+5w9SkGJZ+DRRXWWCywh+yDPVE0KtzeI0andAXDh9yTvs7fLfHH6R4MN9Gutb82k3lD8ugFUCeBVo0xwJULVqFZEFh3KXWruo6KOG79cz2EF7vFApx+skanQPveIMz/80V72KQvb6XNmg6WBhdjqAA==",
"MillisBehindLatest": 0
}
Note the data encoding is not human readable and would need to be parsed/converted to be interpretable. There are many options to build a Kineis consumer such as the KCL.
For purposes of validating the workflow, it may be simpler to locate the workflow in the Step Function Management Console and assert the expected output is similar to the below examples.
Successful CNM Response Object Example:
{
"cnmResponse": {
"provider": "TestProvider",
"collection": "MOD09GQ",
"version": "123456",
"processCompleteTime": "2017-09-30T03:45:29.791198",
"submissionTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:29.791198",
"receivedTime": "2017-09-30T03:42:31.634552",
"identifier ": "testIdentifier123456",
"response": {
"status": "SUCCESS"
}
}
}
Kinesis Record Error Handling
messageConsumer
The default Kinesis stream processing in the Cumulus system is configured for record error tolerance.
When the messageConsumer fails to process a record, the failure is captured and the record is published to the kinesisFallback SNS Topic. The kinesisFallback SNS topic broadcasts the record and a subscribed copy of the messageConsumer Lambda named kinesisFallback consumes these failures.
At this point, the normal Lambda asynchronous invocation retry behavior will attempt to process the record 3 mores times. After this, if the record cannot successfully be processed, it is written to a dead letter queue. Cumulus' dead letter queue is an SQS Queue named kinesisFailure. Operators can use this queue to inspect failed records.
This system ensures when messageConsumer fails to process a record and trigger a workflow, the record is retried 3 times. This retry behavior improves system reliability in case of any external service failure outside of Cumulus control.
The Kinesis error handling system - the kinesisFallback SNS topic, messageConsumer Lambda, and kinesisFailure SQS queue - come with the API package and do not need to be configured by the operator.
To examine records that were unable to be processed at any step you need to go look at the dead letter queue {{prefix}}-kinesisFailure.
Check the Simple Queue Service (SQS) console. Select your queue, and under the Queue Actions tab, you can choose View/Delete Messages. Start polling for messages and you will see records that failed to process through the messageConsumer.
Note, these are only records that occurred when processing records from Kinesis streams. Workflow failures are handled differently.
Kinesis Stream logging
Notification Stream messages
Cumulus includes two Lambdas (KinesisInboundEventLogger and KinesisOutboundEventLogger) that utilize the same code to take a Kinesis record event as input, deserialize the data field and output the modified event to the logs.
When a kinesis rule is created, in addition to the messageConsumer event mapping, an event mapping is created to trigger KinesisInboundEventLogger to record a log of the inbound record, to allow for analysis in case of unexpected failure.
Response Stream messages
Cumulus also supports this feature for all outbound messages. To take advantage of this feature, you will need to set an event mapping on the KinesisOutboundEventLogger Lambda that targets your response-endpoint. You can do this in the Lambda management page for KinesisOutboundEventLogger. Add a Kinesis trigger, and configure it to target the cnmResponseStream for your workflow:
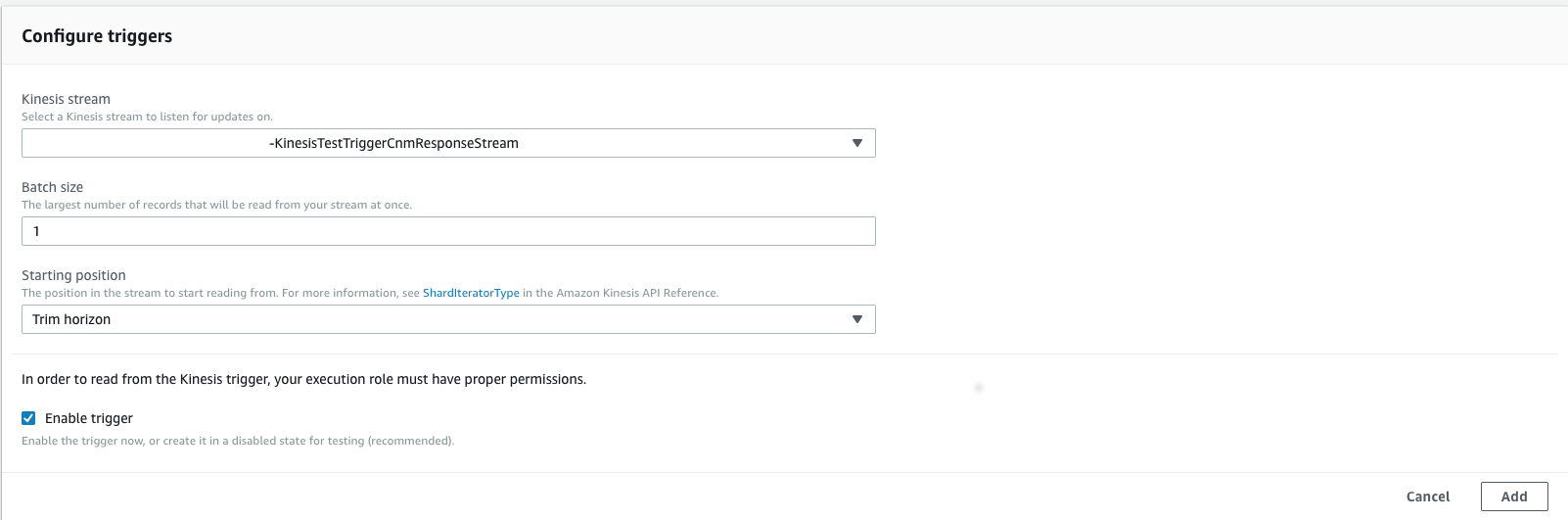
Once this is done, all records sent to the response-endpoint will also be logged in CloudWatch. For more on configuring Lambdas to trigger on Kinesis events, please see creating an event source mapping.