 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
The Svc::Health component monitors the execution health of the software. It does so by pinging active components and checking for a response. It also does optional platform-specific checks.
The requirements for Svc::Health are as follows:
| Requirement | Description | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| HTH-001 | The Svc::Health component shall ping each output port specified in the provided table. | Unit Test |
| HTH-002 | The Svc::Health component shall track the timeout cycles for each component. | Unit Test |
| HTH-003 | The Svc::Health component shall issue a FATAL event if a component fails to return a ping by the specified timeout | Unit Test |
| HTH-004 | The Svc::Health component shall have a command to enable or disable all monitoring | Unit Test |
| HTH-005 | The Svc::Health component shall have a command to enable or disable monitoring for a particular port. | Unit Test |
| HTH-006 | The Svc::Health component shall have a command to update ping timeout values for a port | Unit Test |
| HTH-007 | The Svc::Health component shall stroke a watchdog port while all ping replies are within their limit and health checks pass | Unit Test |
The Svc::Health component has the following component diagram:
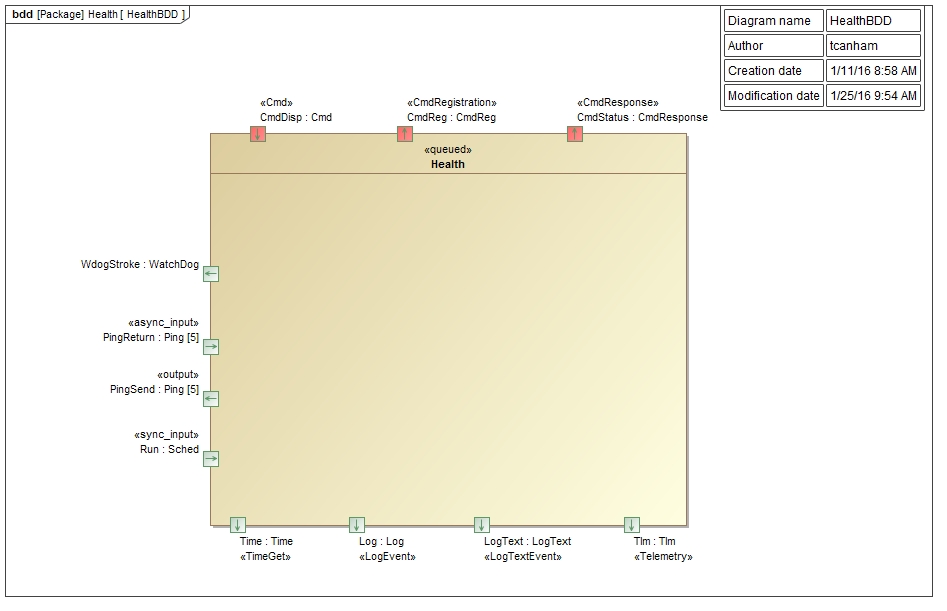
The Svc::Health component uses the following port types:
| Port Data Type | Name | Direction | Kind | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| `Svc::Ping` | PingSend | Output | n/a | Send ping requests from components |
| `Svc::Ping` | PingReturn | Input | Asynchronous | Receive ping responses from components |
| `Svc::Sched` | Run | Input | Synchronous | Execute periodic behavior |
| `Svc::WatchDog` | Wdog | Output | n/a | Send ping requests from components |
The Svc::Health component monitors health by iterating through a table of port numbers and their maximum allowed timeout. The timeout is specified as the number of calls to the SchedIn port. The actual timeout value in wall time will be dependent on the rate at which the port is called. During each SchedIn port call, all the PingSend ports are called with a key. The key is simply a counter value maintained as a private data member. An active component with a Svc::Ping port is required to execute the port handler on the thread of the component. When the handler is invoked, it returns the value of the Svc::Ping port key argument as the argument to the output Svc::Ping port. When the health component receives the return port invocation on the PingReturn port, it sets a status in the tracking table indicating the response was received. In addition to dispatching pings to components, the SchedIn port call checks the status of all the dispatched pings to verify that they have not exceeded the specified timeout. If there is a call that is outstanding but has not timed out, a counter is decremented. The port is not pinged while there is an outstanding ping call. If an active component times out responding to a ping, the Svc::Health component sends a FATAL event. The component has commands to completely turn off monitoring, turn off monitoring for a specific port, or update the timeout values. The updated timeout values or monitoring updates are not stored through a software reset.
The Svc::Health component defines an internal method call doOtherChecks(). It is called at the end of the Run handler, and is meant to be used for platform-specific health checks. Alternate implementations can be added to the mod.mk SRC_ variables. An empty stub has been provided for implementations where nothing extra is needed.
The doOtherChecks() method does the following checks for VxWorks:
The Svc::Health component pings other components and checks for their response:
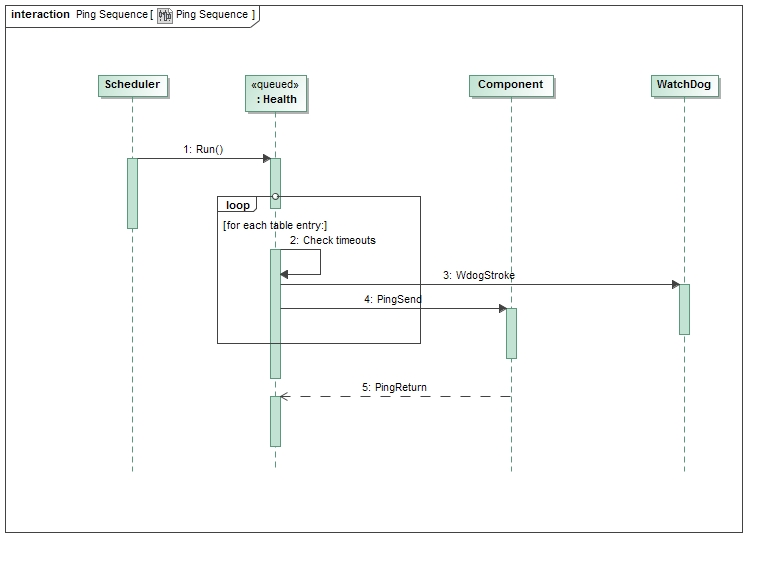
Svc::Health has no state machines.
Svc::Health has no significant algorithms.
TBD
| Document | Link |
|---|---|
| Design Checklist | Link |
| Code Checklist | Link |
| Unit Test Checklist | Link |
The Health unit tests are designed to test interfaces and functionality with the available ports, command processing, telemetry output, EVR and data product generation.
Off-nominal testing contains cases which deal with ping-related issues such as late responses and invalid entries. Every command is also tested with various inputs for thorough validation and code coverage.
When the Health component's schedIn handler is called, each ping entry in the user provided table is checked if it's enabled. If the entry is enabled and empty, a ping is sent out through its corresponding port. If the entry is awaiting a ping response, its counter is checked against a warning threshold and the counter is decremented. If the warning threshold is reached, an EVR and telemetry write are generated. If the fault threshold is reached, a fatal EVR is generated.
This test invokes the schedIn handler for multiple iterations with a provided table of three ping entries. To test nominal conditions, when a ping is received through the test port, a valid ping return is sent back to the component.
For this nominal condition, no EVRs or telemetry are expected.
Requirement verified: HTH-001
This test verifies the requirement that component shall track the timeout cycles for each ping entry. This is validated by having the component ping each entry in the table without responding. The counter for entry is checked after every iteration to see if its value is decremented accordingly. This test will also cause each entry to reach its warning threshold, so the corresponding EVRs and telemetry will be verified.
Requirement verified: HTH-002
This test is similar to 6.1.2, with the difference being that the schedIn handler is ran until the fault threshold for each ping entry is reached. The counters for each entry and expected fault EVRs are both verified.
Requirement verified: HTH-003
In this test, we verify the requirement to enable/disable all monitoring of the ping entries. This is done by running the schedIn handler with monitoring enabled initially with pings sent to each entry with no response from the test. After several iterations and certifying that each entry is being checked, we disable monitoring and invoke the schedIn handler again. During multiple runs of the handler, it is verified that timeouts are not modified and no EVRs are received. Monitoring is then re-enabled and checked if it's working as expected.
Requirement verified: HTH-004
This test is similar to 6.1.4, but instead of enabling/disabling all monitors, each ping entry is enabled then disabled. These actions are verified through the previous methodology of 6.1.4.
Requirement verified: HTH-005
This test verifies the requirement that the component shall have a command to update timeout values for a port entry. This is done by modifying the initial timeout values for each ping entry in the table. These changes are validated by running the schedIn handler and checking for EVRs and telemetry at the updated timeout values.
Requirement verified: HTH-006
This test verifies the requirement that the component shall stroke a watchdog port while all ping are within their limit. This is done by checking the output of the watchdog port and verifying its content.
Requirement verified: HTH-007
This test verifies the functionally of all the provided health commands including the enable/disable monitoring of the ping entries as well as updating timeouts. All commands are validated and verified with nominal inputs.
This test is similar to 6.1.8, but it includes a nominal running of the SchedIn handler while handling incoming commands.
This set of test cases verifies the remaining off-nominal error cases. Each test case is simulated and validated individually.
To see unit test coverage run fprime-util check –coverage
| Date | Description |
|---|---|
| 1/11/2016 | Edits for design review |