 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
FileUplink is an active ISF component. It manages uplink of files to the spacecraft.
| Requirement | Description | Rationale | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISF-FU-001 | FileUplink shall receive file packets, assemble them into files, and store the files in the on-board non-volatile storage. | This requirement provides the capability to uplink files to the spacecraft. | Test |
The design of FileUplink assumes the following:
In the nominal case of file uplink
a. Files are received one at a time. All packets of one file are received before receiving any packets of the next file.
b. Within a file, packets are received in order.
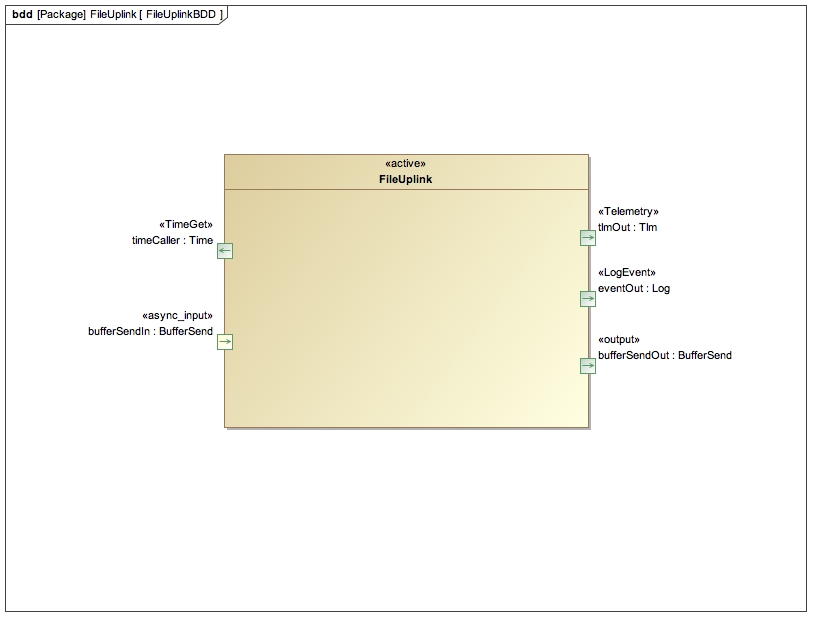
| Name | Type | Role |
|---|---|---|
timeCaller | Fw::Time | TimeGet |
tlmOut | `Fw::Tlm` | Telemetry |
eventOut | `Fw::LogEvent` | LogEvent |
| Name | Type | Kind | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
bufferSendIn | `Fw::BufferSend` | async input | Receives buffers containing file packets. |
bufferSendOut | `Fw::BufferSend` | output | Returns buffers for deallocation. |
FileUplink maintains the following state:
FileUplink expects to receive. The initial value is START.FileUplink asynchronously receives buffers on bufferSendIn. Each buffer contains a file packet. When FileUplink receives a buffer, it (a) determines the type of the file packet in the buffer; (b) takes action as specified in section below corresponding to the packet type; and (c) invokes bufferSendOut to return the buffer for deallocation.
Upon receipt of a START packet, FileUplink does the following:
Upon receipt of a DATA packet P, FileUplink does the following, where I is the sequence index of P:
Otherwise
a. If I is not equal to lastSequenceIndex + 1, then issue a PacketOutOfOrder warning reporting lastSequenceIndex and I.
b. If the packet offset and size are in bounds for the current file, then 1. Using *writeFileDescriptor*, write the file data in the
packet at offset specified in the packet.
2. If there was an error writing the file, then issue a
FileWriteError warning.
c. Otherwise issue a *PacketOutOfBounds* warning.
Upon receipt of an END packet P, FileUplink does the following:
a. If *I* is not equal to *lastSequenceIndex + 1*,then issue a PacketOutOfOrder warning reporting lastSequenceIndex and I.
b. Use *writeFileDescriptor* to do the following: 1. Use the method described in § 4.1.2 of theCCSDS File Delivery Protocol (CFDP) Recommended Standard to compute the checksum value for the file.
2. Compare the value computed in the previous step against thechecksum value in the packet. If the two values are different, then issue a BadChecksum warning.
c. Close the file.
Upon receipt of a cancel packet P, FileUplink does the following:
TBD
| Document | Link |
|---|---|
| Design | Link |
| Code | Link |
| Unit Test | Link |
TODO