 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
Svc::ComQueue is an F´ active component that functions as a priority queue of buffer types. Messages are dequeued and forwarded when a Fw::Success::SUCCESS signal is received in order of priority. Fw::Success::FAILURE signals result in the queues being paused until a following Fw::Success::SUCCESS signal.
Svc::ComQueue is configured with a queue depth and queue priority for each incoming Fw::Com and Fw::Buffer port by passing in a configuration table at initialization. Queued messages from the highest priority source port are serviced first and a round-robin algorithm is used to balance between ports of shared priority.
Svc::ComQueue is designed to act alongside instances of the communication adapter interface and implements the communication queue protocol.
Fw::Success::SUCCESS signal was received| Requirement | Description | Rationale | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVC-COMQUEUE-001 | Svc::ComQueue shall queue Fw::Buffer and Fw::ComBuffer received on incoming ports. | The purpose of the queue is to store messages. | Unit Test |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-002 | Svc::ComQueue shall output exactly one Fw::Buffer or Fw::ComBuffer message on a received Fw::Success::SUCCESS signal. | Svc::ComQueue obeys the communication adapter interface protocol. | Unit Test |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-003 | Svc::ComQueue shall pause sending on the Fw::Success::FAILURE and restart on the next Fw::Success::SUCCESS signal. | Svc::ComQueue should not sent to a failing communication adapter. | Unit Test |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-004 | Svc::ComQueue shall have a configurable number of Fw::Com and Fw::Buffer input ports. | Svc::ComQueue should be adaptable for a number of projects. | Inspection |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-005 | Svc::ComQueue shall select and send the next priority Fw::Buffer and Fw::ComBuffer message in response to Fw::Success::SUCCESS. | Svc::ComQueue obeys the communication adapter interface protocol. | Unit test |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-006 | Svc::ComQueue shall periodically telemeter the number of queued messages per-port in response to a run port invocation. | Svc::ComQueue should provide useful telemetry. | Unit Test |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-007 | Svc::ComQueue shall emit a queue overflow event for a given port when the configured depth is exceeded. Messages shall be discarded. | Svc::ComQueue needs to indicate off-nominal events. | Unit Test |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-008 | Svc::ComQueue shall implement a round robin approach to balance between ports of the same priority. | Allows projects to balance between a set of queues of similar priority. | Unit Test |
| SVC-COMQUEUE-009 | Svc::ComQueue shall keep track and throttle queue overflow events per port. | Prevents a flood of queue overflow events. | Unit test |
The diagram below shows the Svc::ComQueue component.
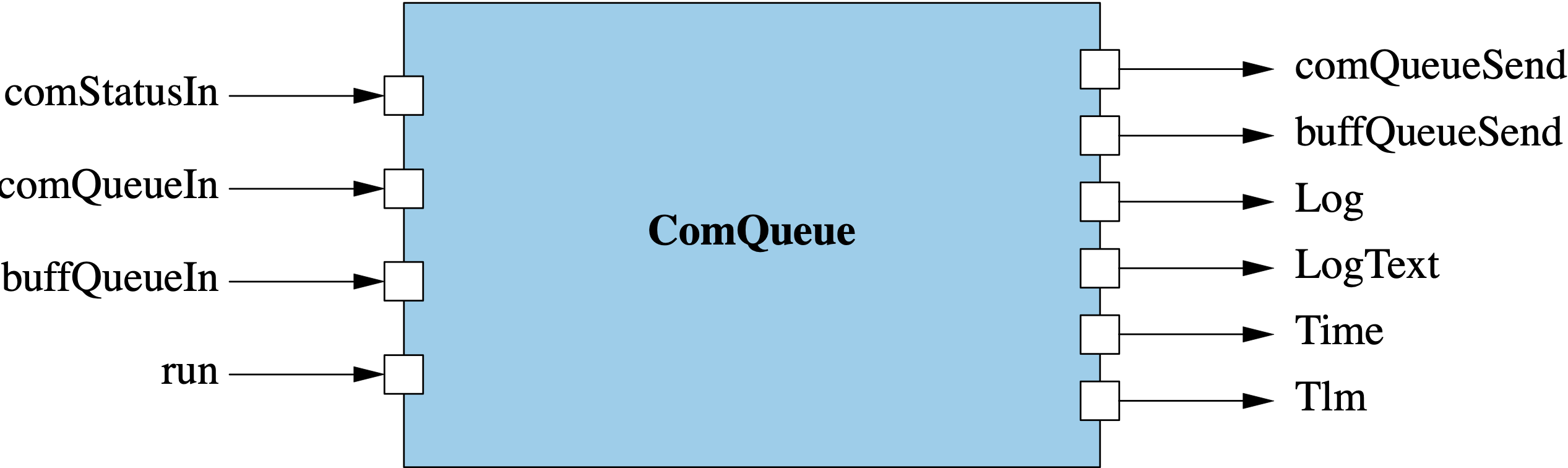
Svc::ComQueue has the following ports:
| Kind | Name | Port Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
output | comQueueSend | Fw.Com | Fw::ComBuffer output port |
output | buffQueueSend | Fw.BufferSend | Fw::Buffer output port |
output | deallocate | Fw.BufferSend | Port for deallocating Fw::Buffer on queue overflow |
async input | comStatusIn | Fw.SuccessCondition | Port for receiving the status signal |
async input | comQueueIn | [ComQueueComPorts] Fw.Com | Port array for receiving Fw::ComBuffers |
async input | buffQueueIn | [ComQueueBufferPorts] Fw.BufferSend | Port array for receiving Fw::Buffers |
async input | run | Svc.Sched | Port for scheduling telemetry output |
event | Log | Fw.Log | Port for emitting events |
text event | LogText | Fw.LogText | Port for emitting text events |
time get | Time | Fw.Time | Port for getting the time |
telemetry | Tlm | Fw.Tlm | Port for emitting telemetry |
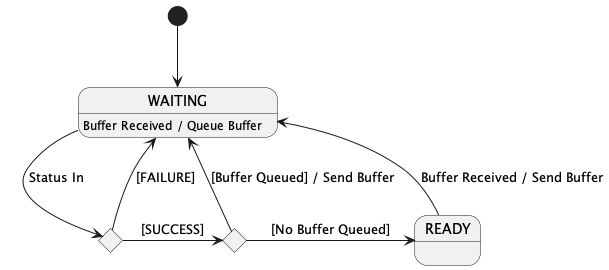
Svc::ComQueue maintains the following state:
m_queues: An array of Types::Queue used to queue per-port messages.m_prioritizedList: An instance of Svc::ComQueue::QueueMetadata storing the priority-order queue metadata.m_state: Instance of Svc::ComQueue::SendState representing the state of the component. See: 4.3.1 State Machinem_throttle: An array of flags that throttle the per-port queue overflow messages.The Svc::ComQueue component runs the following state machine. It has two states:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| WAITING | Svc::ComQueue is waiting on SUCCESS before attempting to send an available buffer |
| READY | Svc::ComQueue had no queued buffers and will send the next buffer immediately when received |
The state machine will transition between states when a status is received and will transition from READY when a new buffer is received. FAILURE statuses keep the Svc::ComQueue in WAITING state whereas a SUCCESS status will either send a buffer and transition to WAITING or will have no buffers to send and will transition into READY state. Buffers are queued when in WAITING state.
Svc::ComQueue has the following constants, that are configured in AcConstants.fpp:
ComQueueComPorts: number of ports of Fw.Com type in the comQueueIn port array.ComQueueBufferPorts: number of ports of Fw.BufferSend type in the buffQueueIn port array.To set up an instance of ComQueue, the following needs to be done:
configure method, passing in an array of QueueConfiguration type, the size of the array, and an allocator of Fw::MemAllocator. The configure method foes the following:The buffQueueIn port handler receives an Fw::Buffer data type and a port number. It does the following:
m_queues instancem_queues is fullIn the case where the component is already in READY state, this will process the queue immediately after the buffer is added to the queue.
The comQueueIn port handler receives an Fw::ComBuffer data type and a port number. It does the following:
m_queues instancem_queues is fullIn the case where the component is already in READY state, this will process the queue immediately after the buffer is added to the queue.
The comStatusIn port handler receives a Fw::Success status. This triggers the component's state machine to change state. For a full description see 4.2.1 State Machine.
The run port handler does the following:
run invocation via telemetry| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| comQueueDepth | Svc.ComQueueDepth | High-water mark depths of queues handling Fw::ComBuffer |
| buffQueueDepth | Svc.BuffQueueDepth | High-water mark depths of queues handling Fw::Buffer |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| QueueOverflow | WARNING_HI event triggered when a queue can no longer hold the incoming message |
Stores the com buffer message, sends the com buffer message on the output port, and then sets the send state to waiting.
Stores the buffer message, sends the buffer message on the output port, and then sets the send state to waiting.
In a bounded loop that is constrained by the total size of the queue that contains both buffer and com buffer data, do: