 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
 |
F´ Flight Software - C/C++ Documentation
devel
A framework for building embedded system applications to NASA flight quality standards.
|
BufferManager is a passive ISF component. It allocates a set of fixed-sized buffers as specified by the user. The overall memory for the buffers is allocated by a memory allocator provided to the component at runtime.
| Requirement | Description | Rationale | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| FPRIME-BM-001 | BufferManager shall allow the specification of multiple bins of buffers based on the size of the buffer | Allows for some optimization of memory usage if buffers of varying sizes are needed | Test |
| FPRIME-BM-002 | BufferManager shall allocate the first buffer larger than the requested size from the set of unallocated buffers, starting with the smallest set of buffers. | If a buffer from a smaller pool is not available, allow using larger buffers to avoid starving the user | Test |
| FPRIME-BM-003 | BufferManager shall return an empty buffer (size = 0) if no buffers are available | Allow the user to decide how to react to no memory | Test |
| FPRIME-BM-004 | BufferManager shall accept empty returned buffers without an assert | Just send a warning to cover the case where an empty buffer is returned by a component | Test |
| FPRIME-BM-005 | BufferManager shall use a provided Fw::MemAllocator instance to request overall buffer memory | Let the user decide where the memory comes from | Test |
| FPRIME-BM-006 | BufferManager shall allow buffers to be returned in any order | Do not restrict the lifetime or usage of buffers | Test |
The design of BufferManager assumes the following:
BufferManager has some maximum number of outstanding allocations, set at component initialization, that is never exceeded.BufferManager has a fixed size, set at component initialization. This fixed size is never exceeded by the outstanding allocations.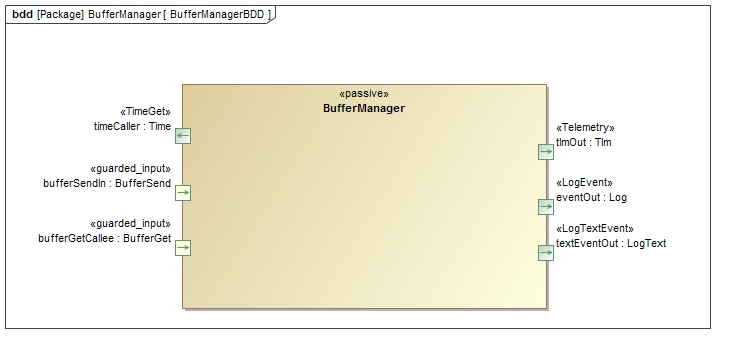
| Name | Type | Role |
|---|---|---|
timeCaller | Fw::Time | TimeGet |
tlmOut | `Fw::Tlm` | Telemetry |
eventOut | `Fw::LogEvent` | LogEvent |
| Name | Type | Kind | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
bufferSendIn | `Fw::BufferSend` | guarded input | Receives buffers for deallocation |
bufferGetCallee | `Fw::BufferGet` | guarded input (callee) | Receives requests for allocated buffers and returns the buffers |
schedIn | `Svc::Sched` | sync input (callee) | writes telemetry values (optional, if the user doesn't need BufferManager telemetry) |
BufferManager maintains the following constants:
BufferManager maintains the following state:
When BufferManager receives a request for a buffer of size s on bufferGetCallee, it carries out the following steps:
Fw::Buffer instance to the user.When BufferManager receives notification of a free buffer on bufferSendIn, it carries out the following steps:
Fw::Buffer instance.The schedIn port is optional. It doesn't need to be connected for BufferManager to function correctly. When BufferManager receives a call on this port, it will write all the defined telemetry values.
The following sequence diagram shows the procedure for sending a buffer from one component to another:
bufferGetCallee port of BufferManager.bufferSendIn port of BufferManager for deallocation.BufferManager will assert under the following conditions:
TBD
Completed.