URLs and filenames
Creating URLs
URLs should be short, memorable, easy to type, and well-structured. Your control over your URL may be limited, but you should do what you can with the pieces you can control.
In the vast majority of cases, everything a user can reach on your site should have a distinct URL that a user can bookmark and use later to reach that same location.
When creating URLs, use dashes to separate words, omit articles
(a/an/the), use the stems of verbs (/make-thing/ rather than
/making-thing/), and avoid extraneous terms.
Domains
Domains should reflect the user’s needs and not those of the organization. If your department is several layers deep in terms of bureaucratic structure, it’s unlikely that this is important to users, and there is likely minimal cost associated with using a more shallow domain.
It’s not necessary to have www. at the start of a domain. This is a
holdover from the early internet. Any domain that has a www level
should also work if that level is omitted.
Domains should not be more than three levels deep in most cases:
18f.gsa.gov is fine, but content-guide.guides.18f.gsa.gov would not
be. It’s rare that more than four levels is justifiable.
At the same time, it’s not necessary to have a two-level domain for everything.
Domain names should be short, using abbreviations unless those are likely to be meaningless to users.
If a domain level has more than one word, you should strongly consider
separating the words with dashes to make sure users read them the way
you intend. If 18F had a project called EARS that for some reason needed
a two-level domain, that domain should be 18f-ears.gov and not
18fears.gov (ears.18f.gov would probably be the ideal).
Domains are case-insensitive. They should be written as lowercase.
Paths
Again, the shorter the better, but long paths are more excusable than long domains.
Paths are typically understood as hierarchies that become increasingly
specific: /content-guide/urls-and-filenames/ reflects that
urls-and-filenames is part of content-guide. If this were a much larger
guide, it’s possible that it could be divided further, for example
/content-guide/urls-and-filenames/creating-urls/.
Each level of a path should make it possible to find the content beneath it:
- The content at the root level should reflect that
/content-guide/is present. /content-guide/should make it easy to findurls-and-filenames/.
Conversely, the user should be able to remove a level from the path and end up at the parent of the original content.
Paths should be designed to be sensible for the user, not to reflect
internal technical or bureaucratic structure. For example, filename
extensions like .php should be avoided as they reflect the internal
technology used on the server (and will not reflect even that if the
site later changes to a different technology).
When separating words in a path, use hyphens. Hyphens are commonly understood by search engines to indicate word breaks (whereas other separators, like underscores, are not).
Paths are case-sensitive. They should be lowercase, regardless of what they contain, as uppercase letters make them more difficult to type (and to remember).
Examples
Domain names
- Starting point:
www.longnamecreationservice.departmentoflongnames.bureauofnames.gov. -
Slight improvement:
longnamecreationservice.departmentoflongnames.bureauofnames.gov.Rationale:
wwwis unnecessary and omitting it makes the URL easier to type. -
Very slight improvement:
long-name-creation-service.departmentoflongnames.bureauofnames.gov.Rationale: Hyphens make the URL easier to read. The same would be true for the other levels of the domain, but we’re assuming you don’t have control over those in these examples.
-
Improvement:
long-name-creation-service.bureauofnames.gov.Rationale: The user doesn’t need the URL to reflect that the service belongs to the Department of Long Names.
-
Better:
lncs.bureauofnames.gov.Rationale: This is shorter and easier to type. However, it relies on users thinking of the service by that abbreviation.
-
Better:
make-long-names.bureauofnames.gov.Rationale: If the users aren’t familiar with that abbreviation, a shorter description of what the service does is better to have as the lowest level of the domain.
Paths
- Starting point:
/services/default/php/forms/departmentoflongnames/longnamecreationservice/index.php?action=create. -
Slight improvement:
/services/default/php/forms/departmentoflongnames/longnamecreationservice/index.php.Rationale: Assuming that creation is the most likely action users will want to take, make it the default and strip the requirement for the query string.
-
Slight improvement:
/services/default/php/forms/departmentoflongnames/longnamecreationservice/.Rationale: The default page should be delivered automatically, making the inclusion of
index.phpunnecessary. Also, hide the technical details (.php). -
Improvement:
/departmentoflongnames/longnamecreationservice/.Rationale: Users don’t need to know the technical setup of the site.
-
Improvement:
/department-of-long-names/long-name-creation-service/.Rationale: Words should be separated with hyphens.
-
Better:
/department-of-long-names/lncs/.Rationale: As above, if the users are familiar with the abbreviation, use it to make the path shorter.
-
Better:
/department-of-long-names/make-long-names/.Rationale: As above, if they aren’t familiar with the abbreviation, use a shorter description of what the server does.
Both
- Starting point:
www.longnamecreationservice.departmentoflongnames.bureauofnames.gov/services/default/php/forms/departmentoflongnames/longnamecreationservice/index.php?action=create. -
Improvement:
make-long-names.bureauofnames.gov/department-of-long-names/make-long-names/.Rationale: This combines the suggestions from the previous two sections.
-
Better:
make-long-names.bureauofnames.gov.Rationale: This is reasonable if the Department of Long Names has only a couple of services that might be popular enough to warrant their own subdomains, particularly if they don’t necessarily fit cleanly into other content and stand alone.
-
Better:
bureauofnames.gov/department-of-long-names/make-long-names/.Rationale: This is reasonable if the Long Name Creation Service is one of many related services that the Department of Long Names provides.
Maintaining URLs
Users constantly bookmark and share web pages, making the maintenance of permanent and long-lasting URLs an important piece of content management. Broken links obscure the internet landscape.
URLs should never stop working.
This is not as technically challenging as it sounds. If the domain — the high-level domain, not subdomains — is lost, the URLs will be lost, but otherwise it’s entirely possible to keep them working. Planning for them to continue working is the first step in any process that involves new URLs.
Whenever possible, maintain original URLs. In all other cases, set up a redirect for outdated URLs and links; this is almost always a painless task for web managers. There are a variety of ways to accomplish this, some of them requiring more technical work than others. It’s most difficult to accomplish when moving from URLs that include query parameters, as some early website systems did. Sensibly-constructed URLs are easier to migrate.
Some examples:
Changing subdomains
If the agency 18F changed their name from 18F to 19G, they would change their domain, so
the new name for their page would be located at
https://pages.19g.gov/content-guide/urls-and-filenames/. They would keep
the 18f.gov domain running, but it would redirect
everything to 19g.gov. Users who entered the old URL would be
redirected and might not notice the URL change.
If they decide to eliminate the pages subdomain and put this directly on
18f.gov, they would do essentially the same thing, keeping this
subdomain and adding a rule to redirect to the same path on 18f.gov.
Changing paths
If, for example, 18F produces lots of content in the future, it might become
sensible to change the path to reflect this, and they might want to have a
guides level, so that the new URL for this page would be:
https://pages.18f.gov/guides/content-guide/urls-and-filenames/. In
this case, they would add a rule that redirects everything starting with
/content-guide/ to /guides/content-guide/.
This also means that URLs, and parts of URLs, should not be re-used.
Once /content-guide/ is used to refer to the guide, they can no longer
use /content-guide/ as the location for something
else in the future, even if they later change the URL for their guide.
Creating filenames
Use hyphens to separate words, just as with URLs.
Lowercase is better, because it’s easier to type and to remember.
Use the right extension — PDFs should have .pdf at the end, JPGs
should have .jpg at the end, etc.
Shorter is better, but the content should be descriptive to the user,
and it’s better to have long descriptive filenames than short obscure
ones. summary-of-pay-gap-findings.pdf is better than paygap.pdf or
smmrypgpfnds.pdf.
If the file content is based on a date or time, include that; the 1998
report for an organization should have 1998 in the filename, a
February issue of a magazine should have the year and the month, and a
PDF of a daily newspaper should have year, month, and date. When
including dates, use the YYYY-MM-DD format, i.e. 2015-10-13.
Avoid the use of special characters beyond the hyphen and period, unless absolutely necessary. Do not include spaces (use hyphens in their place).
Presenting URLs and filenames in text
Whether beginning with the protocol or not, always lowercase URLs in text. Paths are case-sensitive, however, so their casing must be preserved.
In interactive contexts, particularly web pages, URLs (except when used as examples, as throughout this document) should always be active links. When they’re active links, do not include the protocol in the link text.
In non-interactive contexts, such as print, the protocol can be omitted,
assuming http:// and https:// both work and bring the user to the
same place.
There are occasions where URLs should be delimited; use < and > for
this. This is not normally necessary in interactive contexts where the
link is clearly defined, but is most often relevant in email, where the
writer may have to guess at what their email program will turn into a
link. This is particularly true when URL contains spaces.
Filenames are case-sensitive, and their case should be preserved when they are referred to in text; do not capitalize if beginning a sentence with a filename that begins with a lowercase letter. Filenames may need to be delimited in the same way as URLs.
Examples
Capitalization on a web page:
gsa.gov is the General Services Administration site.
Capitalization in print:
gsa.gov is the General Services Administration site.
Delimiting an awkward URL in email:
When you get the chance, could you redirect <example.com/spaces in URLs are bad/> to <example.com/spaces-in-urls-are-bad/>, as per our guidelines, and make the latter the definitive URL for the page?
URL Structure
- The protocol. For example
https://,http://, orftp://. The://is always present. - The domain. For example
18f.gsa.gov. This is “where on the internet” the URL is referring to. Also called:- site
- domain name
- server
- Optional: the port. A number specifying how to access the
content on this particular domain. Not normally used on
production sites. Follows the domain, separated by a colon, for
example
http://dev.example.com:8080. - The path: what resource on the domain the URL is referring to.
If omitted, defaults to
/, the “root level” of the domain. Always starts with a slash, and different levels of resources are separated by slashes. For example:/content-guide/is the path inhttps://pages.18f.gov/content-guide/. - Optional: the query string. Normally contains parameters that
have been submitted to the site, for example with searches.
?q=18f+content+guideis the query string inhttps://www.google.com/search?q=18f+content+guide. - Optional: the fragment. Normally this indicates a specific
section of a page, but can also be used for other things by
web applications.
#mainis the fragment inhttps://pages.18f.gov/content-guide/specific-words-and-phrases/#main.
The protocol should almost always be https:// unless you’re forced to
use http://. Users entering http:// as the protocol should be
redirected to https://. If at all possible, your URL should not
contain a port. Query strings should also be avoided. Fragments can be
used as a helper for the user, but should not be necessary for the user
to find the relevant content.
Link text
It’s important to remember that users of screen readers will often skip from one link to another, skipping the text in between, as a way of “skimming” content.
This ultimately means that link text should be understandable independent of the text surrounding it. Avoid link text like click here, here, learn more, and so forth whenever possible.
For example, instead of:
Click here for more information about our Code of Conduct.
Use:
For more information, see the 18F Code of Conduct.
This has an added benefit of improving search results for sighted users.
Screen reader-only text
Screen readers are audio interfaces. Rather than displaying web content visually for users in a “window” or screen on the monitor, screen readers convert text into synthesized speech so that users can listen to the content. A person using a screen reader is referred to as a screen reader user.
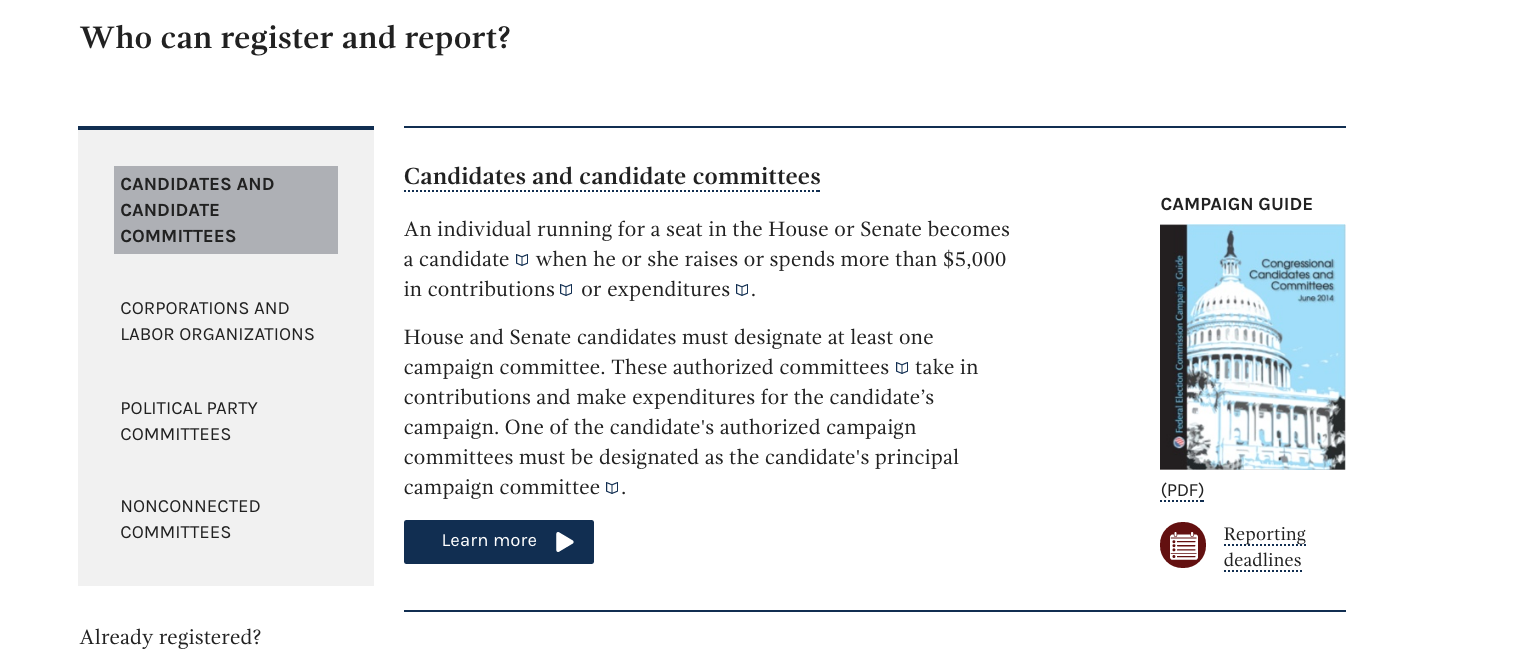
In some situations, descriptive links may be overly verbose or redundant for sighted users. Here’s an example from the betaFEC site:
Here the Learn more link is appropriate for sighted users, but it may be
confusing to screen reader users. In such situations, it’s possible to add
invisible text just for screen reader users. For example, the
Draft U.S. Web Design Standards has a special CSS class called usa-sr-only
for this purpose. Using this class, the aforementioned Learn more link
might be written in HTML like so:
<a href=”essentials-house-and-senate-candidates-and-committees/”>
Learn more
<span class=”usa-sr-only”>
about candidate and candidate committees
</span>
</a>
This would keep the link concise for sighted users, while also providing important context for screen reader users.
If you want to use text intended only for screen readers on your project but are unfamiliar with CSS, ask your project’s front end developer for help. They can create a CSS class for you if one doesn’t already exist. Alternatively, reach out to #g-accessibility or #g-frontend in Slack!