References
- Documents
- Hugin API Reference Manual, Version 7.4, Hugin Expert A/S, 2010
- Sensitivity Analysis, Modeling, Inference and More, (SamIam), Automated Reasoning Group, Computer Science Department, UCLA.
Bayesian Reasoning
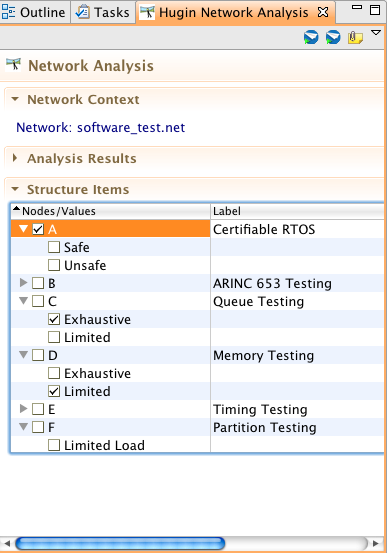
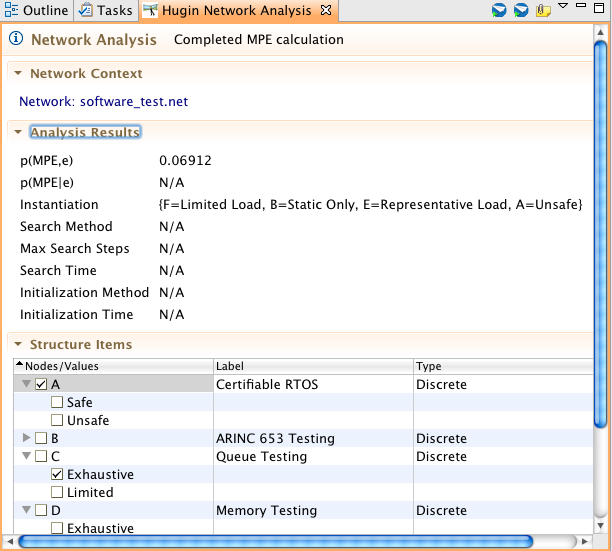
After the analyst creates a Hugin Network describing the problem domain he will want to perform some queries on his network model. We use the SamIam inference engine to support the query calculations. CertWare provides a Network Analysis view which shows the selected network resource file as a structured tree, where the network variables are the branch nodes and the variable states are leaves on each node. Each variable or state is selectable with its checkbox. To assert evidence, click on the corresponding state (these are mutually exclusive in the editor). To select variables for queries, click on their checkboxes. The following figure shows this Network Analysis view with a model selected. The view is also included in the CertWare perspective.
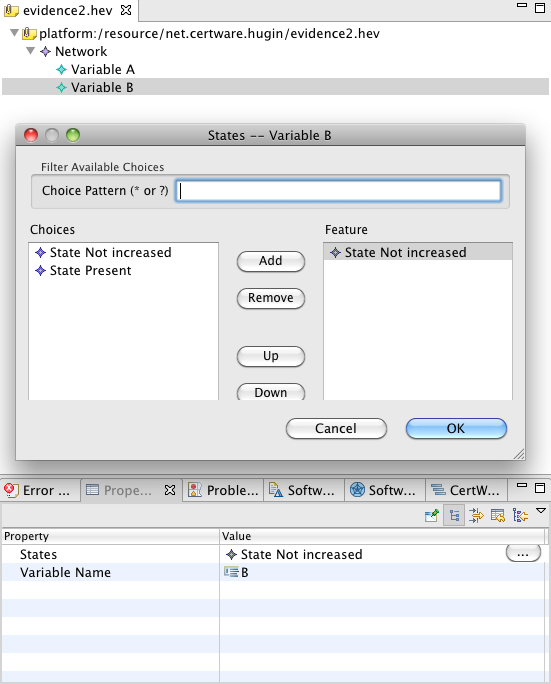
To save evidence selections for future application, CertWare provides an evidence metamodel and editor. The view can create an instance of this model with the current evidence selections, prompting the user where to save the file in the workspace. To recover and apply evidence saved earlier, simply restore the evidence in the selected model. If the model has changed structure, or evidence is applied to a different model, only variable and state matches that succeed will be applied. While it is not necessary to use the evidence model editor, one is available in the workspace (perhaps for generating permutations for testing), and is shown in the following figure.
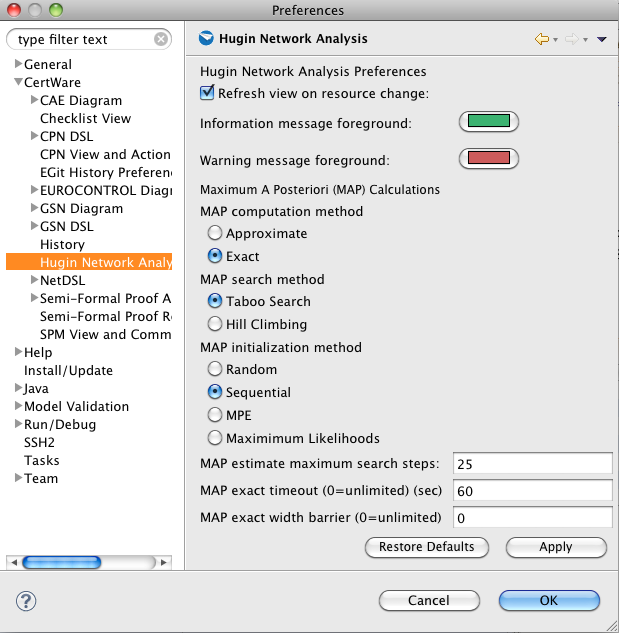
To perform queries in this Network Analysis view, assert the evidence selections, if any, and select the variables of interest for the query results. The toolbar buttons will respond to selections, as will the corresponding items in the view's menu. The queries available at this writing are the maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) and most probable explanation (MPE) calculations. To set up the inference engine preferences see the Network Analysis view's preference page.
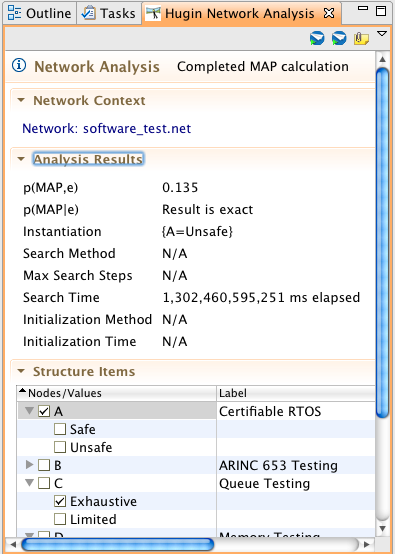
The MAP calculations determine the most likely state of world for each selected MAP variable given the evidence. It computes both p(MAP,e) and p(MAP|e), and can use either approximate or exact values; the approximate methods are most appropriate for large models as the exact algorithm complexity is exponential. The MPE calculation is a special case wherein all of the nodes with unobserved values are selected as MAP variables. In this case only p(MPE,e) is relevant. The following figure shows a sample MAP calculation result as shown in the Network Analysis view. Use the section header buttons to expand or collapse sections of interest. Note there is currently a bug in the display of the search time units of measure.
Finally, the following figure shows a sample MPE calculation result on the same model.
Examples
When creating a new NET file in the workbench, CertWare populates the file with a template that shows most of the correct structure for a typical model. Use this template to edit the problem to be computed in the workbench.
See the evaluation license for legal terms regarding this software.